List the six stages of the pre-referral process and briefly explain each of them.
What will be an ideal response?
1. Initial Concern Regarding a Student’s Progress: This is when someone (teacher, parents, other school administrators) notice a student’s academic or behavioral performance is problematic and is concerned and then that concern is expressed (formally or informally).
2. Information Gathering: This is when the mentor collects different kinds of data to support that their concerns with the student are valid (skill level, background knowledge and experiences, expectations, materials, methods, and techniques used previously, and informal assessments, work samples, and other people).
3. Information Sharing and Team Discussion: A team of mentors (general education teacher, school counselor, specialists) meet together to share their information on the child and discuss where the child and lacking and begin sharing ideas of how intense the child’s intervention should be in order to benefit the child.
4. Discussion of Possible Strategies: At this point the members dive more into the specifics of strategies this child needs in order to get back on track. There can be multiple different strategies for a single child given different kinds of behaviors. The team then concretes a strategy, duration, intensity, and frequency of the intervention.
5. Implementation and Monitoring of Strategies: Most commonly involving the general educator, the intervention plan is then carried out and monitored (including the curriculum based measurement) by those who were a part of the planning-even if that means supporting the teacher.
6. Evaluation and Decision Making: This is the last stage where the pre-referral team reconvenes to review all the collected data from before the intervention and during the intervention to look if the student made any progress. Then the team decides if further intervention needs to take place (if they should continue onto the same plan, figure out a new one, or possibly refer the child to Special Education) or if the child is back on track.
You might also like to view...
Tamara frequently interrupts other children who are talking together. Increasingly, children avoid her. Describe exactly how you would intervene in this situation and provide a rationale for the approach you choose
What will be an ideal response?
The presence or absence of ________ affects the number and intensity of supports needed as adults, levels of independence, level of community presence, and quality of life.
A. parental involvement B. early intervention and preschool services C. physical and occupational therapy supports D. numerical and print literacy skills
All of the following are responsibilities of the program director except:
a. Creating the expectation that all staff cultivate positive relationships with families. b. Providing logistical support such as making the center available for conferences during hours when it is not typically in operation. c. Nurturing a center culture that welcomes and embraces families as partners. d. Translating all teachers' communications with families into their native languages and translating families' responses for teachers.
Looking at the degrees of freedom for a statistic like a t-statistic provides information regarding ______.
a. the size of the sample
b. the sample mean 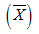
c. whether alpha is one-tailed or two-tailed
d. the population mean (?)