An unexpected event like a drought in the Midwest causing a loss of wheat crops would be an example of
a. a stagflation shock.
b. a supply shock.
c. an input shock.
d. a productivity shock.
b. a supply shock.
You might also like to view...
All of the following are considered to be problems associated with the use of concentration ratios to measure market power except:
A) the market definitions used in their construction may be arbitrary. B) two different markets with the same concentration ratio may have very different distributions of market share among firms used to calculate the concentration ratio. C) consideration of exports and imports generally causes concentration ratios to be overstated. D) concentration ratios are often based on national statistics and may not reflect substantial concentration in a market at a more localized level.
Suppose the working-age population of a fictional economy falls into the following categories: 30 are retired; 45 are stay-at-home parents; 120 are employed full time; 40 are employed part time; 25 are unemployed but are actively looking for
employment; 15 are unemployed and are not actively looking for employment. The official unemployment rate as calculated by the BLS would be A) 9.62%. B) 13.51%. C) 14.55%. D) 20.0%.
According to the graph shown, producing 14 units:
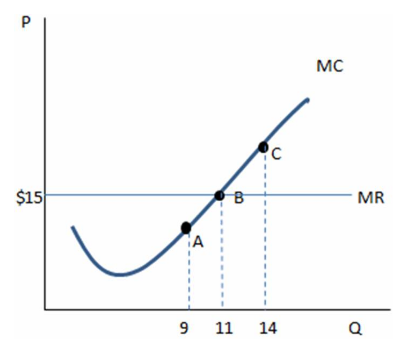
A. is not as profitable as producing 11 units.
B. will earn negative profits.
C. will earn more profits than producing 9 or 11 units.
D. will earn zero profit.
Which of the following is not true of long run equilibrium under monopolistic competition? a. Price equals marginal cost
b. Price equals average cost. c. Price equals minimum average total cost. d. None of the above.