Suppose the price of a liter of soda is $2. If Sara is willing to pay $3 for that liter of soda, her consumer surplus when she buys the soda is:
A. $0.
B. $1.
C. $2.
D. $3.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Which of the following explains why purchasing power parity may not hold perfectly in the long run?
A) Most countries have free markets with limited government regulation. B) Consumer preferences for goods and services across countries are very similar. C) Most countries do not impost trade barriers. D) Some goods and services produced in any country are not traded internationally.
Since 1950, it can be observed that the female participation rate in our labor force has
A) increased. B) decreased. C) stayed constant. D) moved erratically up and down.
Which of the following is the best example of what happens when an equilibrium point is reached?
A. A store that sells its televisions for $999 lowers its price to 899 B. All the stores in a city are selling a certain model of television for 899$ C. some customers decide $899 is too high ad buiy a lower-cost television D. The number of tellevision available at $899 is the same as the number of sales
Refer to the information provided in Figure 2.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.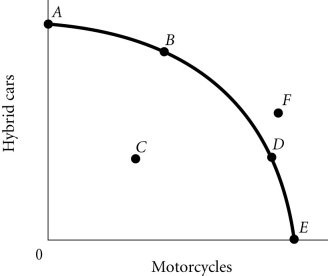 Figure 2.4According to Figure 2.4, a decrease in unemployment may be represented by the movement from
Figure 2.4According to Figure 2.4, a decrease in unemployment may be represented by the movement from
A. A to C. B. C to D. C. B to D. D. B to A.