Movie matinees are priced lower than the evening shows; television advertising costs less when run after midnight. These are examples of what type of price discrimination?
What will be an ideal response?
These are examples of time pricing or price discrimination based on time.
You might also like to view...
Sweet Dreams Corp. has prepared the following financial statements:

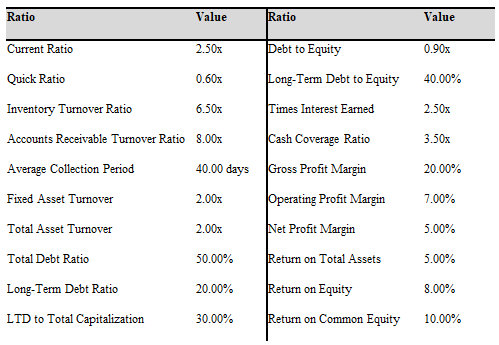
a) Set up a worksheet similar to the one in Exhibit 4-4, page 124, and calculate all of the ratios for Sweet Dreams Corp.
b) Verify the change in 2017 Sweet Dreams Corp’s ROE using the Du Pont method.
c) Using the Altman’s model for privately held firms and public ones, calculate the Z-score for Sweet Dreams Corp. Assume that the market value of Sweet Dreams Corp. is $1,200,000.
d) Calculate Sweet Dreams Corp.’s economic profit for these years and compare it to net income. Assume that the weighted average cost of capital is 12%.
e) Using the following 2017 industry averages, evaluate Sweet Dreams Corp.’s financial situation. Set up a ratio analysis system similar to the one in Exhibit 3-6, page 92.
A product purchase decision usually ends when a consumer recognizes his or her specific need or want
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
As the purchasing manager of a company that designs costumes, Natalie orders yards of fabric in preparation for Halloween. Natalie's duties can be classified under the ________ category of a business process.
A. operations B. sales C. marketing D. outbound logistics E. inbound logistics
Short Corp just issued bonds that will mature in 10 years, and Long Corp issued bonds that will mature in 20 years. Both bonds promise to pay a semiannual coupon, they are not callable or corvertible, and they are equally liquid. Further assume that the Treasury yield curve is based only on the pure expectations theory. Under these conditions, which of the following statements is CORRECT?
A. If the yield curve for Treasury securities is flat, Short's bond must under all conditions have the same yield as Long's bonds. B. If the yield curve for Treasury securities is upward sloping, Long's bonds must under all conditions have a higher yield than Short's bonds. C. If Long's and Short's bonds have the same default risk, their yields must under all conditions be equal. D. If the Treasury yield curve is upward sloping and Short has less default risk than Long, then Short's bonds must under all conditions have a lower yield than Long's bonds. E. If the Treasury yield curve is downward sloping, Long's bonds must under all conditions have the lower yield.