Why does the demand curve for Japanese yen slope down?
What will be an ideal response?
The demand for Japanese yen is derived from the demand for Japanese goods and services. The lower the price of the yen, the more Japanese goods and services that U.S. residents will desire to import. So, the quantity of Japanese yen demanded will increase as the price of the yen falls.
You might also like to view...
Suppose a firm has the following total cost function TC = 100 + 2q2. If price equals $20, what is the firm's output decision? What are its short-run profits?
What will be an ideal response?
If the short-run price elasticity of demand for hospital care is 0.27, then the long-run price elasticity should be
a. greater than 0.27 b. greater than 1.00 c. less than 0.27 d. equal to 0.27 e. less than 0
Maria wishes to buy gasoline and have her car washed. She finds that if she buys 9 gallons of gasoline at $2.50 per gallon, the car wash costs $2, but if she buys 10 gallons of gasoline, the car wash is free. For Maria, the marginal cost of the tenth gallon of gasoline is
A) $2.50. B) zero. C) $2.00. D) 50 cents.
A country has the per-worker production function yt = 6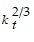 ,where yt is output per worker and kt is the capital-labor ratio. The depreciation rate is 0.1 and the population growth rate is 0.1. The saving function is St = 0.1Yt,where St is total national saving and Yt is total output.(a)What is the steady-state value of capital-labor ratio?(b)What is the steady-state value of output per worker?(c)What is the steady-state value of consumption per worker?
,where yt is output per worker and kt is the capital-labor ratio. The depreciation rate is 0.1 and the population growth rate is 0.1. The saving function is St = 0.1Yt,where St is total national saving and Yt is total output.(a)What is the steady-state value of capital-labor ratio?(b)What is the steady-state value of output per worker?(c)What is the steady-state value of consumption per worker?
What will be an ideal response?