A spaceship of mass 106 kg is to be accelerated to 0.60c. How much energy does this require?
a. 2.3 × 10^22 J
c. 2.5 × 10^23 J
b. 6.0 × 10^22 J
d. 1.5 × 10^23 J
A
You might also like to view...
Mass on a Spring: A 0.50-kg object is attached to an ideal spring of spring constant (force constant) 20 N/m along a horizontal, frictionless surface. The object oscillates in simple harmonic motion and has a speed of 1.5 m/s at the equilibrium position. At what distance from the equilibrium position are the kinetic energy and potential energy of the system the same?
A. 0.017 m B. 0.029 m C. 0.12 m D. 0.17 m
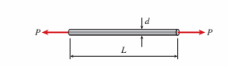
A bar of diameter d 5 18 mm and length L 5 0.75 m is loaded in tension by forces P. The bar has modulus E 5 45 GPa and allowable normal stress of 180 MPa. The elongation of the bar must not exceed 2.7 mm. The allowable value of forces P is approximately:
(A) 41 kN
(B) 46 kN
(C) 56 kN
(D) 63 kN
Based on Planet Z's size, orbital distance, and rotation rate, which of the following properties is it likely to have?
1. a surface crowded with impact craters 2. active tectonics 3. strong winds and violent storms 4. active volcanoes 5. seasons 6. an atmosphere produced by outgassing 7. polar ice caps 8. erosion due to liquid water
In an electromagnetic wave in free space, the electric and magnetic fields are
A) parallel to one another and perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation. B) perpendicular to one another and parallel to the direction of wave propagation. C) perpendicular to one another and perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation. D) parallel to one another and parallel to the direction of wave propagation.