Suppose that the Marginal Social Benefit associated with drinking water quality is estimated to be MSB = 100 – 0.5A,where A is the percentage of mercury abated from drinking water and MSB is measured in millions of dollars. Find the total social benefit (TSB) associated with a federal policy that increases mercury abatement from 20 percent to 30 percent.
What will be an ideal response?
The TSB associated with some abatement level can be found as the area under the MSB function at that level. Therefore, to find the change in TSB associated with the increased mercury abatement from 20 percent to 30 percent, find the TSB at each abatement (A) level, and then find the difference between the two. Graphically, this difference is shown as the shaded area under the MSB curve between the 20 percent and 30 percent abatement levels, as shown in the accompanying figure.
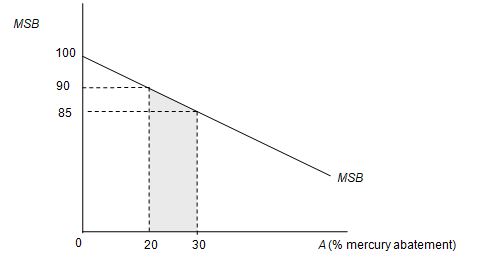
To calculate the shaded area, begin by finding the MSB at each A, i.e., when A = 20, MSB = 100 – 0.5(A) = $90 million, and when A = 30, MSB = 100 – 0.5(30) = $85 million. Now, find the area as (½ * 10 * 5) + (10 + 85) = $875 million.
Alternatively, find the area under MSB when A = 30, which is $2,775 million, and subtract the area under MSB when A = 20, which is $1,900 million, for a difference of $875 million.
You might also like to view...
The official U.S. poverty line for a family is calculated by taking 3 times the annual cost of:
a. public housing. b. basic medical care. c. utilities and transportation. d. a minimal diet.
The marginal propensity to consume (MPC) is the slope of the:
a. GDP curve. b. disposable income curve. c. consumption function. d. autonomous consumption curve.
The savings of individuals or corporations within a country is called:
A. private savings. B. national savings. C. public savings. D. real GDP.
The main policy advice given by the IMF to East Asian countries facing the financial crises of 1997/1998 was
A) raising their domestic interest rates to stabilize the collapsing currencies. B) using their monetary and fiscal policies alone. C) use capital controls. D) adopting a flexible exchange rate system.