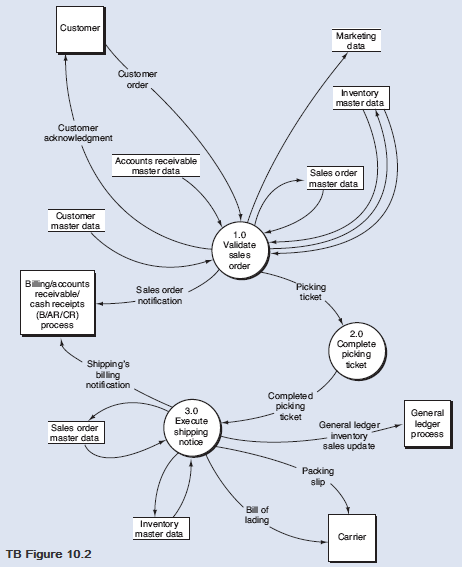
Below is a narrative of the "Validate sales order" portion (i.e., bubble 1.0) of the order entry/sales process
Narrative Description
How does the OE/S process then validate a customer order? First, process 1.1 verifies the availability of the requested inventory by consulting the inventory master data. If a sufficient level of inventory is on hand to satisfy the request, the order is forwarded for further processing, as depicted by the data flow "Inventory available order." Conversely, if a customer orders goods that are not in stock, process 1.1 runs a special back order routine. This routine determines the inventory requirement necessary to satisfy the order and then sends the back order request to the purchasing department. This activity is depicted by the "Back order" data flow, which in reality is a specific type of exception routine (i.e., a specific type of reject stub). If the customer refuses to accept a back order, then the sales event is terminated and the order is rejected, as shown by the "Reject" data flow. Information from the order (e.g., sales region, customer demographics, and order characteristics that reflect buying habits) that has potential value to marketing is recorded in the marketing data store.
After assuring inventory availability, process 1.2 establishes the customer's existence and then evaluates credit. The credit check adds the amount of the order to accounts receivable balances and open sales orders (i.e., orders about to be receivables), and compare that total to the credit limit. If the customer has exceeded their credit limit, the order is rejected.
Upon a successful credit approval, process 1.3 performs the following activities simultaneously:
•
Updates the inventory master data to allocate the quantity ordered to the sales order. The inventory balance could actually be reduced at this time to save a later update of the inventory master data.
•
Updates the sales order master data to indicate that a completed sales order has been created.
•
Disseminates the sales order.
Required:
From the DFD in TB Figure 10.2 and the narrative description above, explode bubble 1.0 into a lower-level diagram showing the details of that process.
You might also like to view...
Earnings per share is an indication of how much:
A) the company has in cash for each share of outstanding common stock. B) the company earned for each share of outstanding common stock. C) the company paid as dividends for each share of common stock held by stockholders. D) the company earned for each share of outstanding common and preferred stock.
Which of the following terms is sometimes used to describe the greater propensity for certain groups to have difficulties in moving out of lower-level jobs:
a. glass basement b. social traps c. underclass d. sticky floor
Brand identity is best defined as
A. a combination of print, guerilla, broadcast, and outdoor advertising to promote a company's products. B. the process of hiring commercial market research agents to conduct a thorough market research before entering a market with unique products. C. a combination of the name, logo, symbols, design, packaging, and image of associations held by consumers. D. the process of creating new product lines within a company to expand and develop the company's product portfolio. E. a method of defining the percentage of loyal, impulsive, and need-based customers for a particular product.
Under the permit system of the Clean Water Act, only industries that discharge unconventional pollutants must have a permit defining the amount of each pollutant that may be discharged under the outlined technology systems stated in the permit
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false