The diamond-water paradox is an example that shows that
A. marginal utility can initially increase and then decrease.
B. necessities like water should have a higher price.
C. there are exceptions to the law of diminishing marginal utility.
D. marginal utility rather than total utility determines what people are willing to pay for a good.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Forecasts based on the extrapolation of observed trends and relationships are likely to be accurate, if ________
A) changes in expectations are properly considered B) policy actions are anticipated C) economic behavior is guided by rational expectations D) policy changes are understood to be permanent
In recent years, which of the following has comprised less than 5% of GDP?
A) imports B) exports C) net exports D) none of the above
Answer the following statement(s) true (T) or false (F)
1. The firms in a cartel act together to achieve a similar outcome as a monopolist. 2. Consumers are the primary beneficiaries of collusive oligopoly due to lower prices. 3. The more firms in a cartel, the more difficult it is for all the firms to reach consensus. 4. Collusive oligopolies are strictly illegal under U.S. antitrust laws. 5. Price leadership involves formal meetings between the price leader and the price followers.
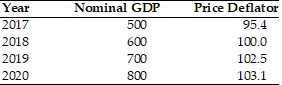 Refer to the above table. Real GDP in 2020 is
Refer to the above table. Real GDP in 2020 is
A. 103.1. B. 824.8. C. 775.9. D. 128.9.