Consider an economy in equilibrium, and assume no change in aggregate demand. An earthquake that destroys many factories across the country would result in a(n):
a. increase in the average price level and a decrease in real GDP.
b. increase in the average price level and no change in real GDP.
c. increase in the average price level and an increase in real GDP.
d. decrease in the average price level and an increase in real GDP.
e. decrease in the average price level and a decrease in real GDP.
a
You might also like to view...
In general, in the 19th century, America
(a) was a low tariff nation because it was believed that free trade brought specialization, efficiency and more rapid economic growth. (b) was a nation that kept its tariffs at about the same levels as England so as not to give the British an advantage. (c) was a high tariff nation which believed, from the days of Alexander Hamilton, that America's industry needed protection from the more industrially advanced England. (d) had a moderate level of tariffs, compared with England, whose main purpose was to provide the federal government with revenues.
Assume the market is in equilibrium in the graph shown at demand D and supply S1. If the supply curve shifts to S2, and a new equilibrium is reached, which of the following is true?
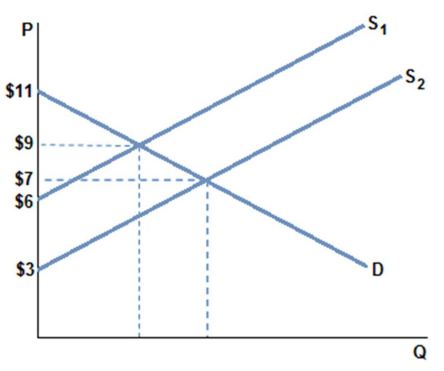
A. Consumer surplus increases, and total surplus increases.
B. Consumer surplus decreases, and total surplus increases.
C. Consumer surplus increases, and total surplus decreases.
D. Consumer surplus decreases, and total surplus decreases.
Recently, banking has become easier with automated teller machines replacing bank tellers. The loss of tellers' jobs is an example of _____
a. cyclical unemployment b. structural unemployment c. frictional unemployment d. underemployment e. voluntary unemployment
Having a chronic trade deficit is a problem, but for countries that have chronic trade surpluses, the consequences are just as problematic
Indicate whether the statement is true or false