Refer to the diagrams, in which AD 1 and AS 1 are the "before" curves and AD 2 and AS 2 are the "after" curves. Other things equal, a decline in net exports caused by the foreign purchases effect of a price-level increase is depicted by the:
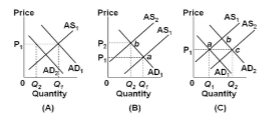
A. shift of the AD curve in panel (A).
B. move from point a to point b in panel (B).
C. shift of the AS curve in panel (B).
D. move from point a to point c in panel (C).
B. move from point a to point b in panel (B).
You might also like to view...
A buyer is said to be a price taker if she:
A) can bargain over the prices of the goods she consumes. B) can purchase any amount of a good at a fixed price provided she has the money to pay for it. C) always pays less than the market-determined price for the goods she is consuming. D) ignores the prices of related goods and considers only the price of the goods she is purchasing.
Typically, consumers respond to an increase in (expected) future income by ________
A) shifting the budget constraint to the left B) increasing both current and future consumption C) saving more to increase future wealth D) waiting until the income is received before changing their consumption behavior
Which of the following is the best example of an oligopolistic? industry?
A) public education
B) the beef market
C) the beauty products industry
D) the pharmaceutical industry
Use the equation of exchange to explain the impact of an increase in the money supply if velocity and output are stable.
What will be an ideal response?