Why would making a permanent change in a monetary aggregate have an effect on exchange rates in a nation?
a. Permanent rates are mostly set by short-run fluctuations in the rate of interest caused by monetary instability.
b. A permanent change is never quite as permanent as policy makers claim-people form expectations on past performance rather than declarations.
c. The central bank is always aware of the effect on exchange rates as it formulates policy, so it is very careful to make small permanent changes that have no effect on exchange rates.
d. Traders form expectations of future exchange rates based on the anticipated long-run effects of monetary operations
Ans: d. Traders form expectations of future exchange rates based on the anticipated long-run effects of monetary operations
You might also like to view...
Refer to Table 2-11. This table shows the number of labor hours required to produce a cell phone and a board foot of lumber in Estonia and Finland
a. Which country has an absolute advantage in the production of cell phones? b. Which country has an absolute advantage in the production of lumber? c. What is Estonia's opportunity cost of producing one cell phone? d. What is Finland's opportunity cost of producing one cell phone? e. What is Estonia's opportunity cost of producing one board foot of lumber? f. What is Finland's opportunity cost of producing one board foot of lumber? g. If each country specializes in the production of the product in which it has a comparative advantage, who should produce cell phones? h. If each country specializes in the production of the product in which it has a comparative advantage, who should produce lumber?
Which of the following is true of an annually balanced federal budget? a. Most economists agree that the federal government should balance its budget just as each household does. b. Such a policy would require the government to increase its spending when tax receipts decrease
c. Such a policy became popular between the 1930s and 1960s. d. Such a policy guarantees that the economy is its potential level. e. Such a policy could worsen a contractionary gap.
When a tax is imposed on a good, the actual incidence of the tax generally
a. falls entirely on the buyer. b. falls entirely on the seller. c. is shared between the buyer and seller. d. is the same as the statutory incidence.
Assume that all firms in this industry have identical cost curves, and that the market is perfectly competitive. 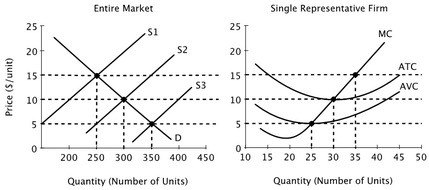 The long-run equilibrium price in this industry is:
The long-run equilibrium price in this industry is:
A. $10 B. $0 C. $5 D. $15