Money supply is linked to the monetary base by the money multiplier. Macroeconomic textbooks tell you that the central bank cannot control the money supply, but it can control the monetary base
As a result, you decide to specify a distributed lag equation of the growth in the money supply on the growth in the monetary base. One of your peers tells you that this is not a good idea for modeling the relationship between the two variables. What does she mean?
What will be an ideal response?
Answer: Although the monetary base is one of the determinants of the money supply, there are other factors, such as interest rates, that have an effect on the money multiplier. Hence there is the problem of omitted variables. If interest rates are correlated with the monetary base, then the OLS estimator will be inconsistent. Furthermore, it is likely that due to financial innovations, dynamic causal effects have changed over time. Finally there is the concern of simultaneous causality bias. If the Federal Reserve changes the monetary base as a result of changes in the money supply, perhaps as a result of targeting, then the monetary base becomes endogenous.
You might also like to view...
Holding large amounts of bank capital helps prevent bank failures because
A) it means that the bank has a higher income. B) it makes loans easier to sell. C) it can be used to absorb the losses resulting from bad loans. D) it makes it easier to call in loans.
If two different fuel sources (e.g., coal and natural gas) are perfect substitutes in the long-run production of energy. How will a profit maximizing firm choose between these two inputs?
A) The firm will only use the input with lower cost B) The firm will use equal amounts of the two inputs, even if one of the inputs has a lower cost C) The firm will only use the input with higher cost D) The firm cannot achieve a profit maximizing level of output under these circumstances
Refer to the information provided in Figure 4.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.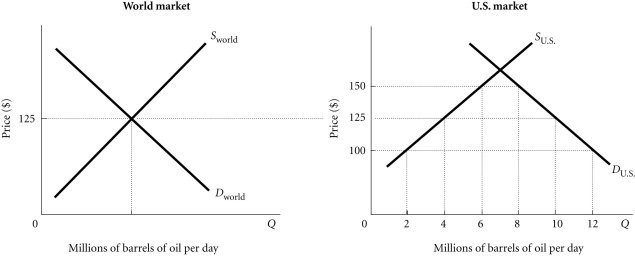 Figure 4.4Refer to Figure 4.4. Assume that initially there is free trade. If the United States then imposes a $25 tariff per barrel of imported oil, the tariff revenue generated will equal
Figure 4.4Refer to Figure 4.4. Assume that initially there is free trade. If the United States then imposes a $25 tariff per barrel of imported oil, the tariff revenue generated will equal
A. $25 million per day. B. $50 million per day. C. $100 million per day. D. $125 million per day.
Related to the Economics in Practice on page 716: In the Kerala region of India, fishermen used cell phones to help connect buyers and sellers, reducing waste. All of the following describe ways in which technology is likely to improve information flow and increase economic efficiency except
A. video conferencing decreases the need for expensive business travel. B. e-mail now makes criminals who commit certain kinds of fraud very difficult to identify and arrest. C. fax technology makes it possible to transmit signed contracts in seconds, allowing the parties to the contract to begin performing their contract duties more quickly. D. high-speed Internet connections allow engineers in developing countries to collaborate with firms all around the world.