Four +6.00-µC point charges are at the corners of a square 2.00 m on each side. What is the electric potential of these charges, relative to infinity, at the center of this square? (k = 1/4??0 = 8.99 × 109 N ? m2/C2 )
A) 76.4 kV
B) 38.2 kV
C) 306 kV
D) 153 kV
E) 61.0 kV
D
You might also like to view...
For an ideal gas,
A) CP = CV for all ideal gases. B) CP > CV for all ideal gases. C) CP < CV for all ideal gases. D) it depends on whether the gas is monatomic or diatomic.
In what geometric way can we determine the absolute distances to the planets?
What will be an ideal response?
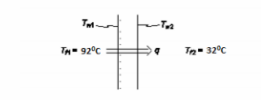
A heat exchanger wall consists of a copper plate 2 cm thick. The heat transfer coefficients on the two sides of the plate are 2700 and 7000 W/( m2 K), corresponding to fluid temperatures of 92 and 32°C, respectively. Assuming that the thermal conductivity of the wall is 375 W/ ( m K), (a) compute the surface temperatures in °C, and (b) calculate the heat flux in W/ m2.
GIVEN
• Heat exchanger wall, thickness (L) = 2 cm = 0.02 m
• Heat transfer coefficients
? hc1 = 2700 W/(m2 K)
? hc2 = 7000 W/(m2 K)
• Fluid temperatures
? Tf1 = 92°C
? Tf2 = 32°C
• Thermal conductivity of the wall (k) = 375 W/( m K) FIND (a) Surface temperatures (Tw1, Tw1) in °F (b) The heat flux (q/A) in W/m2. ASSUMPTIONS
• One dimensional heat transfer prevails
• The system has reached steady state
• Radiative heat transfer is negligible
SKETCH
Pure elements can be transformed into entirely different elements by
A) radioactive decay. B) transmutation. C) both of these D) neither of these