A plastics factory emits water pollutants into a nearby river. The marginal private cost of producing plastics and the marginal external cost of the pollutants are both constant with respect to the quantity of plastics produced
If the demand for plastics is downward sloping, what happens to the socially optimal level of output and market price if the demand curve for plastics shifts rightward? A) Optimal price and quantity increase
B) Optimal price increases, optimal quantity remains unchanged
C) Optimal price remains unchanged, optimal quantity increases
D) Optimal price and quantity remain unchanged
C
You might also like to view...
In 1980, one Zimbabwean dollar was worth 1.47 U.S. dollars. By the end of 2008, the exchange rate was one U.S. dollar to 2 billion Zimbabwean dollars
When an economy experiences rapid increases in the price level such as what occurred in Zimbabwe, the economy is said to experience A) inflation. B) stagflation. C) hyperinflation. D) deflation.
Which of the following groups are typically harmed by unexpected inflation?
a. lenders b. borrowers c. pensioners on fixed incomes d. both (a) and (c).
With parity pricing in agriculture, farmers
a. earn higher incomes now than nonfarmers b. fared relatively well during the Depression years of the 1930s c. have seen a persistent downward movement in their purchasing power d. did relatively poorly during the 1920s e. face a declining demand for food in the United States
You are the Minister of Trade for a small island country with the following annual PPC: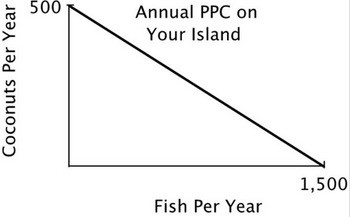 You are negotiating a trade agreement with a neighboring island with the following annual PPC:
You are negotiating a trade agreement with a neighboring island with the following annual PPC: 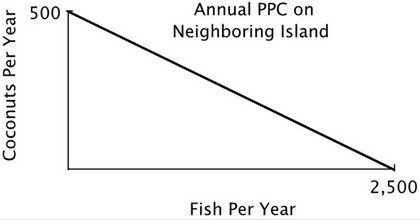 Both islands specialize exclusively in the product for which they have a comparative advantage. You have agreed to give 350 coconuts to the other island in exchange for 1,300 fish. After the trade the other island has a total of ________ coconuts and ________ fish.
Both islands specialize exclusively in the product for which they have a comparative advantage. You have agreed to give 350 coconuts to the other island in exchange for 1,300 fish. After the trade the other island has a total of ________ coconuts and ________ fish.
A. 850; 1,200 B. 350; 1,500 C. 350; 1,200 D. 500; 1,200