Describe the anatomical and physiological features of the respiratory system that limit the establishment of pathogenic organisms
What will be an ideal response?
When air enters the upper respiratory tract, it passes through the paranasal sinus cavities. These cavities are lined with mucous membranes which secrete mucous to trap microbes and debris. The mucous is swept toward the nose and mouth for expulsion by cilia, hair-like projections lining the airway. In the pharynx, the epiglottis is a cartilage structure that seals the entry to the lower respiratory tract while swallowing, preventing the entry of food, beverages, and associated microorganisms to the lungs. The lower respiratory tract airways which include the trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles are lined with ciliate mucous membranes which trap microbes and debris and sweep them upward away from the lungs. This is called the mucociliary escalator. Respiratory infection symptoms such as a runny nose, cough, and sneezing help to expel pathogens but also provide a means for the pathogen to move to the next host. The respiratory tract has an abundant microbiome, even in the lungs. Microbiome members may prevent the establishment of pathogens by competing with pathogens for space and producing antimicrobial peptides.
You might also like to view...
The nuclear envelope is a single lipid layer.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
Aerobic respiration became established as a result of
the evolution of a. the first proto-cells. b. the first true cells. c. metabolism. d. the cyclic pathway of photosynthesis. e. the noncyclic pathway of photosynthesis.
Refer to Figure 29-1. The structure labeled 1 is:
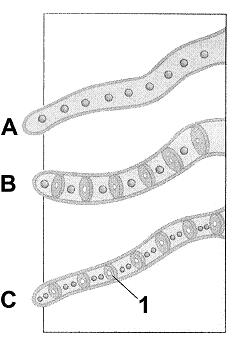
a. a conidium.
b. a perforated septum.
c. a hypha.
d. a basidium.
e. a spore
Mannitol salt agar (MSA) only allows the growth of halophiles (salt-loving microbes). Among the halophiles, mannitol fermenters release acid that turns the pH indicator yellow; mannitol nonfermenters leave the medium red. Onto MSA you inoculate a halophilic mannitol nonfermenter and a nonhalophilic mannitol nonfermenter. Here the medium acts as a ________ medium.
A. enrichment B. selective and differential C. selective D. differential