For the data provided in Problem 15-3, determine (a) minimum length of crest vertical curves, and (b) minimum length of sag vertical curves, using the rate of vertical curvature method, when joining two segments at maximum grade, (c) maximum superelevation, and (d) maximum degree of curve (use fs = 0.15) (Degrees-minutes-seconds).
What will be an ideal response?
(a) Using Equation 15.12, L= kA
From Table 15.4, k = 44
L = 44 (8– (–8))
L = 704 ft
(b) Using Equation 15.12, L = kA
From Table 15.5, k = 64
L = 64 (8– (–8))
L = 1024 ft
(c) Maximum superelevation
Maximum values of superelevation can be as high as 0.12 but vary from
state to state. In Virginia, emax = 0.08 for rural roads.
(d) Maximum degree of curve
Find the minimum radius
R = u2 / [15(e + fs)]
Assuming emax = 0.08 and fs = 0.15
Rmin = (402/15) (1/(0.08 + 0.15)) = 463.77 ft
Find the maximum degree of curvature
Using Equation 15.20, R = 5729.6/D
463.77 = 5729.6/D
D = 12.35445º = 12º 21’ 16”
You might also like to view...
Good conductors have electrons that are difficult to knock out of their orbits.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
Draw the output waveshape of an unrectified LVDT in the following figure when the core is perfectly centered, the core is above center, and the core is below center.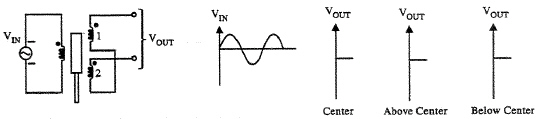
What will be an ideal response?
The capacitor in the circuit of Fig. 16.39 is initially uncharged. Find v?(t) for t>0.
 figure 1.png)
What effect does the daily range have on heat gain?
A) Areas with a high daily range can take advantage of natural cooling that occurs at night, so the cooling HTMs can be a little smaller. B) Areas with a high daily range experience higher temperatures, so the cooling HTMs are higher. C) Areas with a high daily range generally do not require any cooling. D) Areas with a high daily range generally require equipment with more latent cooling capacity.