In a perfectly competitive situation, the profit-maximizing hiring situation for all inputs being used is where
A) the MRP of each input is equal to the price of each input.
B) the MRP of each input is greater than the price of each input.
C) the MRP of each input is less than the price of each input.
D) There is no relationship between MRP and the prices of the inputs.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is a final good or service?
A. Coffee grounds you use to make your coffee every morning B. Coffee grounds used by a coffee shop to make your coffee every morning C. Coffee grounds used by Edy's to make coffee ice cream D. None of these is a final good or service.
The total economic cost of producing a good or service is called the
a. comparative value of construction. b. social consequence of resources. c. marginal valuation of output. d. opportunity cost of production.
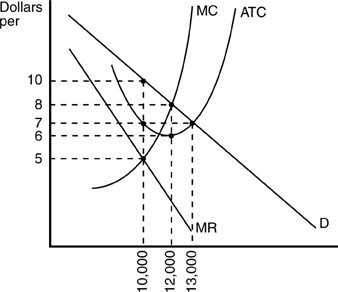 In the above figure, the profit-maximizing output and price for this monopolistically competitive firm are
In the above figure, the profit-maximizing output and price for this monopolistically competitive firm are
A. 10,000 units at a price of $5 per unit. B. 10,000 units at a price of $10 per unit. C. 12,000 units at a price of $8 per unit. D. 13,000 units at a price of $7 per unit.
Refer to the information provided in Table 20.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow. Table 20.4GermanyChileBeerWineBeerWine(cases)(cases)(cases)(cases)75030 060152412453018 24304512 361560 6 48075 0 60 Refer to Table 20.4. Before specialization, Germany produces 45 cases of beer and 30 cases of wine, and Chile produces 18 cases of beer and 24 cases of wine. After specialization, the increase in beer production is
A. 0 cases of beer. B. 2 cases of beer. C. 8 cases of beer. D. 12 cases of beer.