Bond energies increase in going from C-N (lowest) to C-O to C-F (highest). Explain this trend based upon the atomic sizes of these atoms as deduced from their positions in the periodic table.
A. In going from nitrogen to oxygen to fluorine, the atoms get smaller. This means a greater nuclear charge, which translates into stronger chemical bonds.
B. In going from nitrogen to oxygen to fluorine, the atoms get larger. This means a greater nuclear charge, which translates into stronger chemical bonds.
C. In going from nitrogen to oxygen to fluorine, the atoms get smaller. This means that the bonding atoms are closer together, which translates into a greater bond energy.
D. In going from nitrogen to oxygen to fluorine, the atoms get larger. This means that the bonding atoms are farther apart, which translates into a greater bond energy.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
The acceleration of gravity is opposed by the atmosphere in the form of:
A) drag. B) viscosity. C) thermal inversions. D) winds.
Present atmospheric methane (CH4 ) concentrations are at approximately________ ppb
A) 750 B) 1000 C) 1500 D) 1800
If an earthquake occurred near the oceanic trench in this figure, which one of the following hazards is likely to threaten the town of Ashton?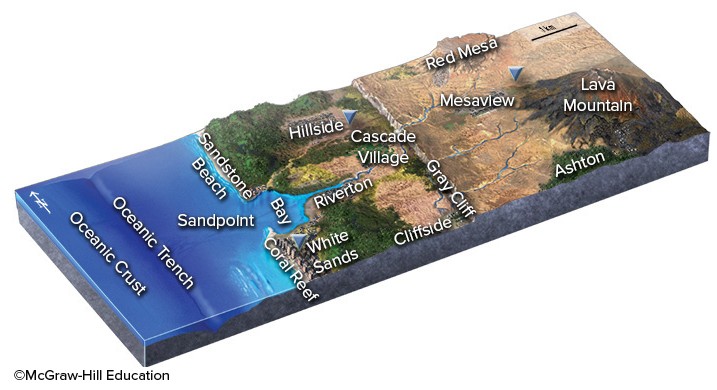
A. landslides and other slope failures caused by shaking B. liquefaction of soils and other weak materials because of shaking C. destruction by a tsunami D. All of these choices are correct.
Using your knowledge of photosynthesis and cell respiration, draw a picture of the hydrogen cycle and the oxygen cycle. (Hint: Consult the 4 cycles in the book for guidance.)
What will be an ideal response?