Suppose that consumers become more pessimistic about the future and, as a result, reduce their consumption by $10 billion. If the marginal propensity to consume is 0.80, how will this $10 billion reduction in consumption affect the equilibrium level of real GDP?
A. Real GDP will decrease by $8 billion.
B. Real GDP will decrease by $10 billion.
C. Real GDP will decrease by $40 billion.
D. Real GDP will decrease by $50 billion.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
The most important factor in reversing the economic decline of 1929-1933 was that
A. the federal government finally balanced its budget. B. the stock market began to rise. C. people became more optimistic. D. the federal government began to spend a huge amount of money.
An office supply store sells a ream of printer paper at a fixed price of $4.50. Which of the following is a term used by economists to describe the money received from the sale of an additional ream of paper?
A) pure profit B) gross earnings C) marginal costs D) marginal revenue E) net benefit
This graph depicts the demand for a normal good. 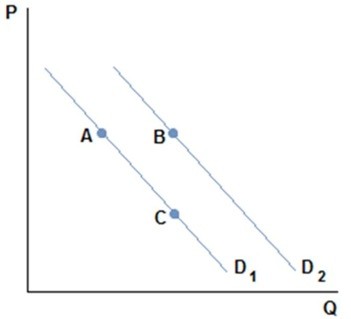 Suppose Johnny was consuming a normal good at point A in the figure shown, but has just received a raise at work. Johnny's demand may:
Suppose Johnny was consuming a normal good at point A in the figure shown, but has just received a raise at work. Johnny's demand may:
A. increase to point B. B. be unaffected. C. drop to zero. D. increase to point C.
Refer to the graphs shown, which depict a perfectly competitive market and firm in a constant-cost industry. If market demand decreases from D0 to D1, in the long run: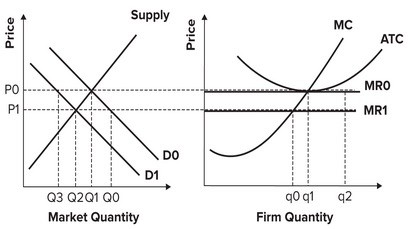
A. some firms will exit this market and the price will return to P0. B. new firms will enter this market and the price will remain at P1. C. new firms will enter this market and the price will return to P0. D. some firms will exit this market and the price will remain at P1.