Figure 7-16
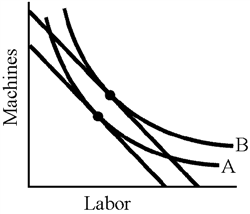
In Figure 7-16, as we move from A to B,
a.
the relative price of machines falls.
b.
total cost falls.
c.
output increases.
d.
labor becomes less productive relative to capital.
c
You might also like to view...
When the Federal Reserve increases the money supply, at the previous equilibrium interest rate households and firms will now have
A) the amount of money that they want to hold. B) more money than they want to hold. C) less money than they want to hold. D) to sell Treasury bills.
The price-output combination that maximizes profits for a monopolist occurs at the point where
A) total revenues and total costs are equal. B) the difference between total revenues and total costs is the greatest. C) total revenues are the greatest. D) the elasticity of demand equals one.
Figure 17-1
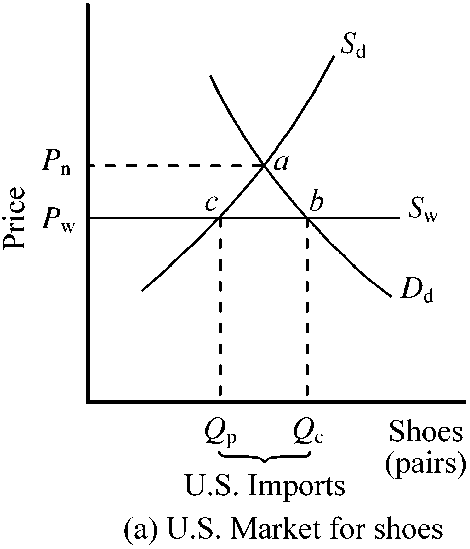
In , in the absence of trade, the domestic price of shoes would be Pn. If the United States moved from a no-trade situation to free trade, which of the following would happen?
a.
The domestic price of shoes would rise, and domestic consumption would fall.
b.
Both the domestic price of shoes and domestic consumption would rise.
c.
Both the domestic price of shoes and domestic consumption would fall.
d.
The domestic price of shoes would fall, and domestic consumption would rise.
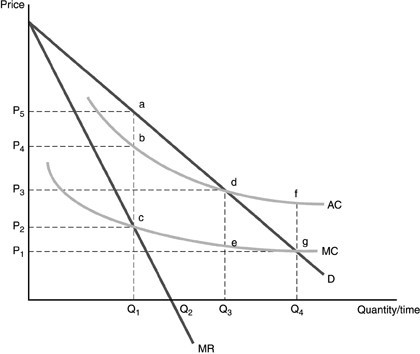 Refer to the above figure. What are the price and quantity if this monopolist is required to use average cost pricing?
Refer to the above figure. What are the price and quantity if this monopolist is required to use average cost pricing?
A. P2, Q1 B. P1, Q4 C. P3, Q3 D. P5, Q1