The purchasing power parity method of comparing income levels across countries
a. calculates the cost of purchasing a common bundle of goods in each country and then uses this price index to convert each country's income to a common currency.
b. uses the exchange rate to convert the income level of each country to a common currency.
c. uses the prime interest rate in each country to convert the income level of each country to a common currency.
d. calculates the ratio of imports relative to exports in each country and then uses this ratio to convert each country's income to a common currency.
A
You might also like to view...
Scarcity guarantees that
A) demands will exceed wants. B) wants will exceed demands. C) demands will be equal to wants. D) most demands will be satisfied.
In terms of economic growth, educated workers are generally:
A. more productive. B. less productive. C. less healthy. D. happier.
Cost curves in the long run differ from cost curves in the short run
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
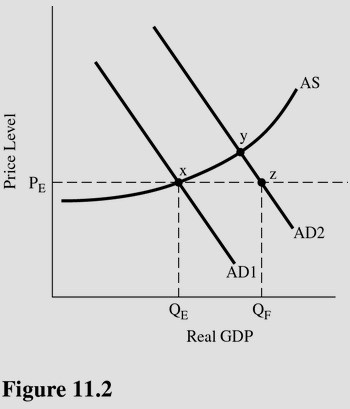 Assuming QF is the full employment equilibrium then a shift from AD1 to AD2 in Figure 11.2 will
Assuming QF is the full employment equilibrium then a shift from AD1 to AD2 in Figure 11.2 will
A. Eliminate the GDP gap. B. Cause significant inflation. C. Worsen the existing unemployment problem. D. Reduce, but not close, the GDP gap.