What are the effects of migration on the real wages and output of a low-wage nation and a high-wage nation? What are the simplifications used to analyze these effects?
What will be an ideal response?
The migration of workers increases the real wages and reduces the output of a low-wage nation while it reduces the real wages and increases the output of a high-wage nation. The gain in output of the high-wage nation outweighs the loss in output of the low-wage nation, increasing economic efficiency and producing a net gain in world output. There are several simplifications used to arrive at these conclusions. First, the demand for labor is greater in the high-wage nation because its labor is more productive due to more capital, advanced technology, and better infrastructure. Second, we assume that neither nation experiences substantial long-term unemployment and that labor quality in the two countries is the same. Finally, we suppose that migration has no cost, occurs solely in response to wage differentials and is unimpeded by law in either country.
You might also like to view...
Which of the following algebraic forms for a demand curve yields an isoelastic demand curve?
A) Q = a - b log(P) + c log(I) B) Q = a - bP + cI C) log(Q) = a - b log(P) + c log(I) D) log(Q) = bP + cI
Which one of the following is an example of passive policy making?
A) introducing expansionary monetary policy to combat a recession B) introducing expansionary monetary policy to combat inflation C) introducing expansionary fiscal policy to combat a recession D) following a predetermined monetary policy rule
Contingent workers are those who have no regular employment arrangement (such as a 40-hour week), but rather work as and where there is work to be done.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
If the budget line shifts from BB to bb in the diagram, we can infer that the:
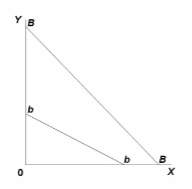
A. price of Y has increased and the price of X has decreased.
B. price of Y has decreased and the price of X has increased.
C. prices of both X and Y have increased.
D. prices of both X and Y have decreased.