Trace through the Keynesian cause-and-effect sequence. An increase in the money supply will cause the interest rate to
a. fall, boosting investment and shifting the AD curve to the right, leading to an increase in real GDP
b. fall, boosting investment and shifting the AD curve to the right, leading to a decrease in real GDP
c. rise, cutting investment and shifting the AD curve to the right, leading to an increase in real GDP
d. rise, boosting investment and shifting the AD curve to the left, leading to an increase in real GDP
e. fall, cutting investment and shifting the AD curve to the left, leading to a decrease in real GDP
A
You might also like to view...
Refer to the below graphs. (Assume that the pre-migration labor force in Country A is 100 and that it is 150 in country B.) The migration of labor will:
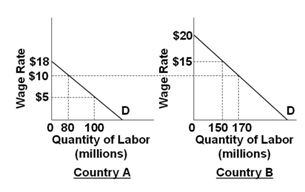
A. Increase domestic output in both countries
B. Decrease domestic output in both countries
C. Increase domestic output in country A and decrease domestic output in country B
D. Decrease domestic output in country A and increase domestic output in country B
If the economy experiences an inflationary gap, a contractionary monetary policy will
A) increase real GDP and increase the price level. B) increase real GDP and decrease the price level. C) decrease real GDP and increase the price level. D) decrease real GDP and decrease the price level.
All of the following are functions of the Federal Reserve System EXCEPT
A. to supply the economy with fiduciary currency. B. to act as the government's fiscal agent. C. to provide loans to developing countries. D. to hold depository institutions' reserves.
Total revenues
A. are not the same as total receipts from the sale of output. B. equal gross revenues minus all expenses of the firm. C. equal the price per unit times the total quantity sold. D. are defined as the quantity sold divided by price.