Most firms are not monopolies in the real world because
a. firms usually face downward-sloping demand curves
b. supply curves slope upward
c. price is usually set equal to marginal cost by firms
d. monopolies are not efficient
e. there are substitutes for most goods
E
You might also like to view...
Haley has 20 hours to devote to work or leisure. If she wants to increase her income, she must increase both her labor and leisure hours at the same time
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
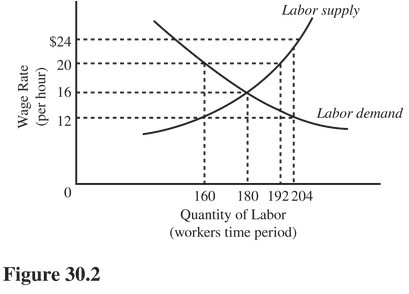 In Figure 30.2, a minimum wage of $12 will result in
In Figure 30.2, a minimum wage of $12 will result in
A. A surplus of 20 workers. B. A shortage of 32 workers. C. A shortage of 44 workers. D. No shortage or surplus of workers.
Which of the following most closely approximates the conditions of a monopolistically competitive market?
A. The market for Grade A eggs, which is characterized by a large number of firms producing a homogeneous product. B. The restaurant industry, which is characterized by firms producing a differentiated product in a market with low entry barriers. C. Local cable television service, where a licensed supplier competes with firms offering satellite service. D. The market for jumbo aircraft, where one major domestic firm competes with one major foreign firm.
Juan purchased a parking pass to a specific lot from the university for $600. Another student, Cara, wants to park there because it's close to her dorm, but cannot because it is full. The Coase Theorem suggests that which of the following negotiations would lead to an optimal outcome?
A. Cara pays Juan $500 for his parking pass B. Cara pays Juan $400 to buy another parking pass C. Cara pays Juan $650 for his parking pass D. Cara buys a pass to another lot for $400 and trades that with Juan