In 1995–7, tax revenue as a percent of GDP
(a) was roughly equal between developing and developed countries.
(b) was a few percentage points higher for developed than for developing countries.
(c) was a few percentage points lower for developed than for developing countries.
(d) was much higher (approximately double) for developed countries than for developing countries.
(e) was much higher (approximately double) for developing countries than for developed countries.
D
You might also like to view...
The economy pictured in the figure below has a(n) ________ gap with a short-run equilibrium combination of inflation and output indicated by point ________. 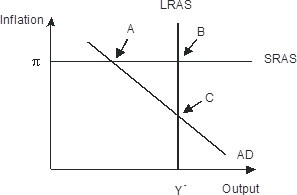
A. recessionary; B B. recessionary; C C. recessionary; A D. expansionary; A
When a society cannot produce all the goods and services people wish to have, the economy is experiencing
a. scarcity. b. surpluses. c. inefficiencies. d. inequalities.
The aggregate demand curve is:
A) vertical if full employment exists. B) horizontal when there is considerable unemployment in the economy. C) downsloping because of the interest-rate, real-balances, and foreign purchases effects. D) downsloping because production costs decrease as real output rises.
In the _________, if profits are not possible, the perfectly competitive firm will seek out the quantity of output where _____________________.
a. long run; production increases b. short run; fixed costs can be reduced c. short run; losses are smallest d. long run; fixed costs can be eliminated