Starting from long-run equilibrium, a large tax increase will result in a(n) ________ gap in the short-run and ________ inflation and ________ output in the long-run.
A. recessionary; lower; potential
B. expansionary; lower; potential
C. expansionary; higher; potential
D. recessionary; lower; lower
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Based on this model, it is apparent that there is a
Use thefollowing information for any or all of Questions 16 through 18. Suppose the marginal benefits and marginal costs of tire production in the U.S. are modeled as follows, where Q is in millions: MSB = 12 – 0.4Q MPB = 12 – 0.3Q MSC = MPC = 2 + 0.1Q a. negative production externality b. positive external benefit c. consumption externality measured as MEB = – 0.1Q d. negatively sloped MEC function
Which of the following will most likely cause an increase in the long-run aggregate supply curve?
a. a reduction in the general level of prices b. an increase in the general level of prices c. an improvement in technology that substantially reduces the cost of generating energy d. an increase in taxes that makes it more expensive for Americans to import crude oil
When can two countries gain from trading two goods?
a. when the first country can only produce the first good and the second country can only produce the second good
b. when the first country can produce both goods, but can only produce the second good at great cost, and the second country can produce both goods, but can only produce the first good at great cost
c. when the first country is better at producing both goods and the second country is worse at producing both goods
d. Two countries could gain from trading two goods under all of the above conditions.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 25.1 below to answer the question(s) that follow.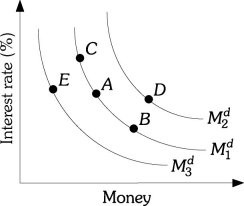 Figure 25.1Refer to Figure 25.1. A movement from Point B to Point D can be caused by
Figure 25.1Refer to Figure 25.1. A movement from Point B to Point D can be caused by
A. a decrease in nominal income. B. an increase in the interest rate. C. an increase in nominal income. D. a decrease in the interest rate.