The purpose of deregulating banks during the 1980s was to:
a. eliminate the risk that banks incurred
b. allow banks to compete with other financial institutions.
c. allow U.S. banks to compete with foreign banks.
d. help consumers earn more interest.
e. decrease the cost of banking regulation.
b
You might also like to view...
Depositors have a strong incentive to show up first to withdraw their funds during a bank crisis because banks operate on a
A) last-in, first-out constraint. B) sequential service constraint. C) double-coincidence of wants constraint. D) everyone-shares-equally constraint.
Cyclical unemployment:
a. causes unemployment statistics to be understated. b. causes unemployment statistics to be overstated. c. occurs because of recessions. d. occurs because of technological innovations in production. e. only occurs with a zero inflation rate.
Because public goods are
a. excludable, people have an incentive to be free riders. b. excludable, people do not have an incentive to be free riders. c. not excludable, people have an incentive to be free riders. d. not excludable, people do not have an incentive to be free riders.
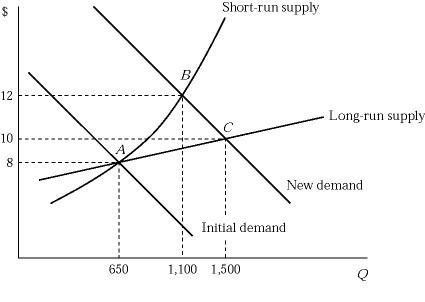
 Figure 6.5 shows the short-run and long-run effects of an increase in demand of an industry with increasing cost. The market is in equilibrium at point A, where 100 identical firms produce 6 units of a product per hour. If the market demand curve shifts to the right, what will happen to an individual firm's profit?
Figure 6.5 shows the short-run and long-run effects of an increase in demand of an industry with increasing cost. The market is in equilibrium at point A, where 100 identical firms produce 6 units of a product per hour. If the market demand curve shifts to the right, what will happen to an individual firm's profit?
A. Each firm earns a positive profit at point B. B. Each firm earns a zero profit at point B because the market is perfectly competitive. C. The profit of each firm decreases as more firms enter the market and share the benefits of an increase in demand pushing the market from point A to point B. D. None of these