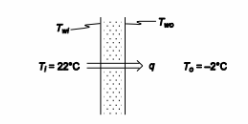
On a cold winter day, the outside wall of a home is exposed to air temperature of –2°C when the inside temperature of room is at 22°C. As a result of this temperature gradient, there is heat loss through the wall to the outside. Consider the convective heat transfer coefficients for the air inside the room and at the outside wall surface to be respectively 12.0 and 28.0 W/(m2 K). If the composite room wall is modelled as a plane wall with thermal resistance per unit area of 0.5 m2 K/W, determine the temperature at the outer surface of the wall as well as the rate of heat flow through the wall per unit area. If the homeowner were to consider using a fiberglass insulation on the inside wall surface for reducing this heat loss by 50 %, what is the required thickness of this layer and the
outside wall temperature for this case?
GIVEN
• Heat transfer through a plane wall
• Air temperature
? Inside wall (Ti) = 22°C
? outside wall (To) = –2°C
• Heat transfer coefficient
? Inside wall ( ci h ) = 12 W/(m2 K)
? Outside wall ( co h ) = 28 W/(m2 K)
• Thermal resistance of a unit area (A Rw) = 0.5 (m2 K)/W FIND (a) Temperature of the outer surface of the wall (Two) (b) Rate of heat flow through the wall per unit area (q/A) (c) Thickness of fiberglass insulation inside wall surface (d) Outside wall temperature with fiberglass insulation
ASSUMPTIONS
• One dimensional heat flow
• Steady state has been reached
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
Thermal conductivity
Fiber glass (k) =0.035 W/m K
SKETCH
The thermal circuit for the wall is shown below
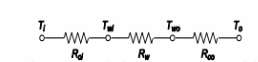
The rate of heat transfer can be used to calculate the temperature of the outer surface of the wall,
therefore part (b) will be solved first.
(b) The heat transfer situation can be visualized using the thermal circuit shown above. The total heat
transfer through the wall,
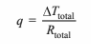
The three thermal resistances are in series, therefore
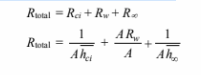
The heat flow through the wall is
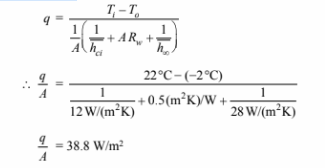
(a) The temperature of the outer surface of the wall can be calculated by examining the
convective heat transfer from the outside of the wall
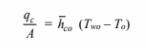
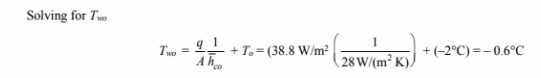
With fiber glass included as insulation, total resistance becomes
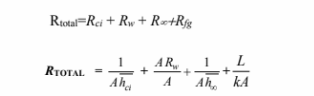
For reducing heat loss by 50 % the overall resistance should be doubled, thus
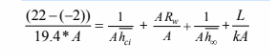

The temperature of the outer surface of the wall can be calculated by examining the convective heat
transfer from the outside of the wall
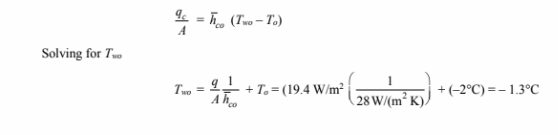
You might also like to view...
Constant Acceleration Kinematics: A car is traveling with a constant speed of 30.0 m/s when the driver suddenly applies the brakes, causing the car to slow down with a constant acceleration. The car comes to a stop in a distance of 120 m. What was the acceleration of the car as it slowed down?
A. 3.75 m/s2 B. 4.00 m/s2 C. 4.25 m/s2 D. 4.50 m/s2 E. 4.75 m/s2
The main energy transformation that occurs while an electric blender is mixing your orange juice is
A) electric E ? kinetic E. B) chemical E ? thermal E. C) electric E ? chemical E. D) kinetic E ? electric E. E) thermal E ? kinetic E.
A toy gyroscope (a.k
a. a top) consists of a solid disk with a thin rod projecting perpendicular to the center of the disk. The rod, which serves as the rotational axis for the gyroscope, projects on both sides of the disk. The gyroscope is placed with one end of the axis on the surface of the table, and spun so that the rotation of the disk viewed from above is counterclockwise. Alas, the axis of rotation is not quite perpendicular table surface and so the gyroscope precesses. Viewing from above, with the end of the axis in contact with the table staying in the same spot, in what direction does the other end of the axis of the gyroscope precess? a. The precession is clockwise. b. The precession is counterclockwise. c. In the northern hemisphere the precession is clockwise, but in the southern hemisphere it is counterclockwise. d. In the northern hemisphere the precession is counterclockwise, but in the southern hemisphere it is clockwise.
High-speed stroboscopic photographs show that the head of a golf club of mass 200 grams is traveling at 55.0 m/s just before it strikes a 46.0-gram golf ball at rest on a tee. After the collision, the clubhead travels (in the same direction) at 40.0 m/s. Find the speed of the golf ball just after impact