Refer to the normal-form game of price competition shown below. 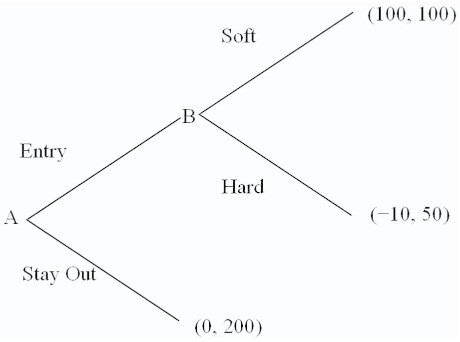 Firm B is the incumbent facing potential entry from its rival, firm A. Firm A's strategies consist of {entry, stay out}. Firm B's strategies are then {hard if entry; hard if stay out; soft if entry; soft if stay out}. Find the non-subgame Nash equilibrium to this game, if one exists.
Firm B is the incumbent facing potential entry from its rival, firm A. Firm A's strategies consist of {entry, stay out}. Firm B's strategies are then {hard if entry; hard if stay out; soft if entry; soft if stay out}. Find the non-subgame Nash equilibrium to this game, if one exists.
A. There is no non-subgame Nash equilibrium to this game.
B. Firm A plays {entry}; firm B plays {soft if entry}.
C. Firm A plays {stay out}; firm B plays {hard if entry}.
D. Firm A plays {entry}; firm B plays {hard if entry}.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
According to public choice theory, low voter turnouts may be the result of cost-benefit calculations on the part of voters
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Your parents have given you a new car on your 16th birthday for which they paid about $24,000. Assume this is also the price you would get if you decided to sell the car a month after getting it. The monthly costs of driving the car are $100 for oil changes and $200 for gas. If you decide to keep the car, the total costs of the car to you this month will be
A. $2,300. B. $24,300. C. $300. D. $0.
If your firm is producing a good at a level where marginal revenue equals marginal cost, and price is less than average variable cost, then in the short run your firm should:
A. shut down and suffer a loss equal to your fixed costs. B. continue to produce, but increase output. C. continue to produce the same amount. D. continue to produce, but decrease output.
When a person's income decreases, the slope of the individual's budget constraint stays the same because:
A. the relative prices of the goods haven't changed. B. everything is relatively more expensive now. C. everything is relatively less expensive now. D. the prices of the goods change in the same proportion.