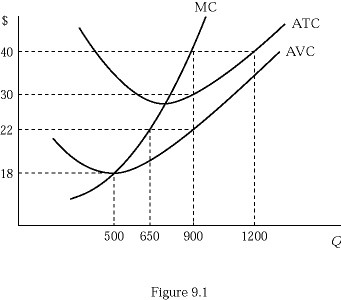
 Figure 9.1 shows the cost structure of a firm in a perfectly competitive market. If the market price is $40, the firm's profit maximizing output level is:
Figure 9.1 shows the cost structure of a firm in a perfectly competitive market. If the market price is $40, the firm's profit maximizing output level is:
A. 500.
B. 650.
C. 900.
D. 1,200.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Answer the following statement(s) true (T) or false (F)
1. When a competitive firm earns zero profit, the market price is equal to both the firm's average and marginal costs. 2. In a competitive constant-cost industry, all firms have the same break-even price. 3. A government subsidy would allow all firms in a competitive constant-cost industry to earn a positive profit in the long run. 4. Sunk costs cannot affect a firm's short-run supply, but they can affect its long-run decision to exit the industry. 5. If the market price is currently above the shut-down price, the firm will be making positive profits.
For the recessions in the United States since the 1950s,
A) unemployment falls on average by 2 percentage points during the 12 months after a recession begins. B) unemployment rises on average about 5 percentage points during the 12 months after a recession begins. C) cyclical unemployment has been non-existent. D) unemployment rises on average by about 1.2 percentage points during the 12 months after a recession begins.
The largest single traded good (by value) in recent years has been
A) automobiles. B) wheat. C) televisions, stereos, and VCRs. D) steel.
A discount shoe manufacturer's advertisement suggests that they are almost as good as the name brands but better value. The shoe manufacturer believes that the advertisement will
a. Make the demand for its product more elastic b. Make his customers more price sensitive c. Cause people to directly compare his product to the name brands d. All of the above