1) Longest period of the cell cycle. 2) The division of the cytoplasm, which occurs at the end of mitosis and meiosis. 3) A phase in meiosis in which homologous pairs are separated from each other. 4) A phase in mitosis in which the chromosomes line up at the center of the cell. 5) The exchange of maternal and paternal forms of genes in prophase I. 6) A phase in mitotic division in which the sister chromatids are pulled apart by the spindle fibers. 7) A phase in mitotic division in which a nuclear membrane forms around each group of chromosomes at the two poles. 8) This cell possesses only a single set of chromosomes. 9) A specific segment of the chromosome's DNA that directs the synthesis of a single protein. 10) The method of reshuffling genes by randomly aligning them in metaphase I.
A) Interphase
B) Anaphase I
C) Metaphase
D) Crossing over
E) Anaphase
F) Telophase
G) Gene
H) Haploid
I) Cytokinesis
J) Independent assortment
Answer:
1. A
2. I
3. B
4. C
5. D
6. E
7. F
8. H
9. G
10. J
You might also like to view...
After 5,730 years, we can predict that half the molecules of 14C will have been converted into ________
a. 14N b. 32P c. 12C d. 60Co
Which type of cell contains a nuclear membrane?
a. Eukarya b. Prokarya c. Bacteria d. Archaea
The sharp peak of estradiol secretion during the ovarian cycle
A. stimulates the secretion of LH and ovulation. B. stimulates growth of the uterine lining. C. inhibits progesterone production. D. inhibits the secretion of LH and FSH. E. stimulates completion of meiosis I.
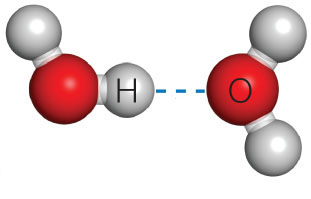
A. covalent bond B. ionic bond C. hydrogen bond D. polar covalent bond E. hydrophobic interaction