How does an expansionary monetary policy affect aggregate expenditures according to the bank lending channel?
What will be an ideal response?
In the bank lending channel, an expansionary monetary policy causes aggregate expenditure to increase for two reasons: (1 ) the increase in households' and firms' spending from the drop in interest rates, and (2 ) the increased availability of bank loans. In other words, if banks expand deposits by lowering interest rates on loans, the amounts that bank-dependent borrowers can borrow and spend increases at any real interest rate.
You might also like to view...
Other things equal, when the real interest rate rises, C, I and NX ________ and real GDP will ________ relative to potential GDP
A) decrease; decrease B) decrease; increase C) increase; increase D) increase; decrease
The impact of the national debt on the? economy's unemployment is an example of
A. irrational economics. B. macroeconomics analysis. C. microeconomic analysis. D. behavioral economics.
We can say that a contract is able to prevent moral hazard when
A) it eliminates production inefficiencies due to moral hazard without shifting risk to risk-averse people. B) it eliminates production inefficiencies due to moral hazard without shifting risk to risk-loving people. C) it shifts risk to risk-loving people. D) it eliminates production inefficiencies due to moral hazard and shifts risk to risk-averse people.
Refer to the diagram and assume the economy is initially at point b 1 . Point c 1 represents:
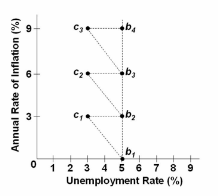
A. a stable position because reality and expectations are consistent.
B. a stable position because full employment and a constant annual inflation rate are
represented.
C. an unstable situation because government will undertake contractionary policies.
D. an unstable situation because nominal wage rates will increase.