Currently. the price of consuming housing 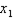 is lowered by the fact that home mortgage interest is tax deductible. Suppose the government proposed to eliminate this implicit subsidy of your housing consumption, raising the price from
is lowered by the fact that home mortgage interest is tax deductible. Suppose the government proposed to eliminate this implicit subsidy of your housing consumption, raising the price from 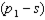 to
to
src="https://sciemce.com/media/3/ppg__cognero__Chapter_07_Income_and_Substitution_Effects_in_Consumer_Goods_Markets__media__9b711c52-06c1-4848-984d-2ca85addf439.PNG" style="vertical-align: -8px;" width="17px" height="28px" align="absmiddle" />. At the same time, the government lowers the tax on other consumption, lowering the price from 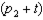 to
to 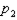 .
.
a. Write down your original budget constraint assuming the consumer has income I.
b. Suppose the utility function 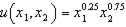 captures your tastes, and suppose
captures your tastes, and suppose 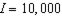 ,
,  ,
, 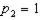 ,
, 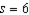 and
and 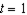 . Write out the utility maximization problem for this consumer prior to any policy change.
. Write out the utility maximization problem for this consumer prior to any policy change.
c. How much housing and other goods will this consumer consume prior to any policy change?
d. How much would this consumer be willing to pay to get the policy change implemented?
What will be an ideal response?
a. 
b. 
c. 
d. We first have to solve for the bundle the consumer would consume if she paid the maximum amount she is willing to pay to get the policy change implemented. The maximum she is willing to pay is an amount that will leave her with the same utility that she had before the policy --- and that utility is  . At the post-policy prices, the expenditure necessary to reach this utility level is determined by solving
. At the post-policy prices, the expenditure necessary to reach this utility level is determined by solving
 .
.
This gives us the bundle  At the post-policy prices, this bundle costs
At the post-policy prices, this bundle costs  --- which implies that the consumer is willing to pay as much as
--- which implies that the consumer is willing to pay as much as  to get the policy implemented. (Without rounding errors, this amount comes out to be $2523.26.)
to get the policy implemented. (Without rounding errors, this amount comes out to be $2523.26.)
Economics
src="https://sciemce.com/media/3/ppg__cognero__Chapter_07_Income_and_Substitution_Effects_in_Consumer_Goods_Markets__media__9b711c52-06c1-4848-984d-2ca85addf439.PNG" style="vertical-align: -8px;" width="17px" height="28px" align="absmiddle" />. At the same time, the government lowers the tax on other consumption, lowering the price from 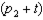
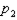
a. Write down your original budget constraint assuming the consumer has income I.
b. Suppose the utility function 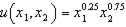
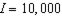

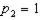
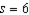
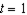
c. How much housing and other goods will this consumer consume prior to any policy change?
d. How much would this consumer be willing to pay to get the policy change implemented?
What will be an ideal response?

b.

c.

d. We first have to solve for the bundle the consumer would consume if she paid the maximum amount she is willing to pay to get the policy change implemented. The maximum she is willing to pay is an amount that will leave her with the same utility that she had before the policy --- and that utility is
 . At the post-policy prices, the expenditure necessary to reach this utility level is determined by solving
. At the post-policy prices, the expenditure necessary to reach this utility level is determined by solving
This gives us the bundle 


You might also like to view...
Why do very small differences in annual growth rates amount to big differences in the degree of long-term economic growth?
A) because the slower-growing countries save too much B) because the annual growth rate is compounded over time C) because the faster-growing countries gain a political advantage over poorer countries, and use that advantage for their economic gain D) because the slower-growing countries don't export enough
The value of the marginal product of labor is the:
A) value of the output produced by all the workers in a firm. B) contribution of an additional unit of labor to a firm's revenue. C) extra output that is produced by hiring an additional unit of labor. D) amount of output produced by the first unit of labor hired by a firm.
The theory that our population would grow too quickly relative to our food supply is associated with
A. Adam Smith. B. Karl Marx. C. Thomas Malthus. D. John Maynard Keynes.
What are the two major problems facing the health care system?
What will be an ideal response?