An 8.0 kg object has a moment of inertia of 1.00 kg 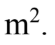 What torque is needed to give the object an angular acceleration of 1.5
What torque is needed to give the object an angular acceleration of 1.5 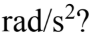
A. 3.0 N•m
B. 2.5 N•m
C. 2.0 N•m
D. 1.5 N•m
E. 1.0 N•m
D. 1.5 N•m
You might also like to view...
The data points in this diagram represent the measured speeds and distances of various galaxies, and the solid line represents a best fit to these data. The trend indicated by the solid line is known as
A) Hubble's law. B) Leavitt's law. C) the inverse square law for light. D) Kepler's third law.
An electron is in an infinite square well that is 2.6 nm wide
What is the smallest value of the state quantum number n for which the energy level exceeds 100 eV? (h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ? s, mel = 9.11 × 10-31 kg, 1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19) A) 43 B) 45 C) 44 D) 42 E) 41
Water pressurized to 3.5 × 105 Pa is flowing at 5.0 m/s in a horizontal pipe which contracts to 1/3 its former area. What are the pressure and velocity of the water after the contraction?
A. 2.5 × 105 Pa, 15 m/s B. 3.0 × 105 Pa, 10 m/s C. 3.0 × 105 Pa, 15 m/s D. 4.5 × 105 Pa, 1.5 m/s E. 5.5 × 105 Pa, 1.5 m/s
A plane moving 200 m/s horizontally fires a projectile with speed 50 m/s in a forward direction 30.0° below the horizontal. At that instant, what is the speed of the projectile with respect to a stationary observer on the ground?
A) 245 m/s B) 250 m/s C) 268 m/s D) 293 m/s