Refer to the table below. The perfectly competitive firm has a random demand with a 25 percent chance of being $5 and a 75 percent chance of being $9. What quantity should the firm produce to maximize its expected profit?
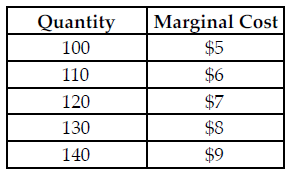
The above table summarizes the marginal cost of production at various quantity levels for a perfectly competitive firm.
A) 110
B) 100
C) 130
D) 120
C) 130
You might also like to view...
The price elasticity of demand for a product is a measure of the:
a. extent of competition in the market for the product. b. change in the quantity purchased of the product relative to a change in a consumer's income. c. change in the quantity demanded of the product due to changes in factors other than price. d. degree of consumer responsiveness to changes in the price of the product. e. percentage change in the prices of two related products.
In a typical year, how accurate are forecasts of inflation and real GDP?
a. within 8-10 percentage points b. within 2-3 percentage points c. within 3/4 of 1 percentage point d. within 1/4 of 1 percentage point
It is possible to purchase diplomas from diploma mills. The situation in which the degrees are more important than the knowledge they are supposed to represent is called:
A. accreditation. B. credentialism. C. cretinism. D. diplomacy.
A contractionary monetary policy causes
A. higher interest rates, which increases the foreign demand for U.S. financial instruments, which causes interest rates to decrease. There is no effect on net exports. B. lower interest rates, which decreases the foreign demand for U.S. financial instruments, raising the international price of the dollar and increasing net exports. C. higher interest rates, which increases the international price of the dollar and decreases net exports. D. higher interest rates, which decreases the foreign demand for U.S. financial instruments, raising the international price of the dollar and increasing net exports.