Two infinitely large black plane surfaces are 0.3 m apart and the space between them is filled by an isothermal gas mixture at 811 K and atmospheric pressure consisting of 25% CO2, 25% H2O, and 50% N2 by volume. If one of the surfaces is maintained at 278 K and the other at 1390 K respectively, calculate
(a) the effective emissivity of the gas at its temperature
(b) the effective absorptivity of the gas to radiation from the 1390 K surface
(c) the effective absorptivity of the gas to radiation from the 278 K surface
(d) the net rate of heat transfer to the gas per square meter of surface area
GIVEN
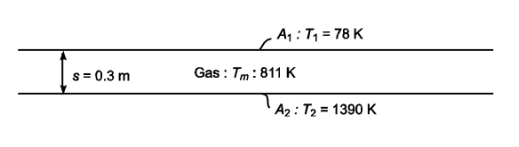
Two infinitely large black plane surfaces with an isothermal gas mixture between them
Distance between surfaces (s) = 0.3 m
Gas mixture temperature (Tm) = 811 K
Gas mixture pressure = 1 atm
Gas contents: 25% CO2, 25% H2O, 50 % N2 by volume
Surface temperatures
T1 = 278 K
T2 = 1390 K
FIND
(a) The effective emissivity of the gas at its temperature (? mix)
(b) The effective absorptivity of the gas to radiation from A1
(c) The effective absorptivity of the gas to radiation from A2
(d) The net rate of heat transfer to the gas per square meter of surface are (qm/A)
ASSUMPTIONS
Steady state
Convection is negligible
SKETCH
(a) The partial pressures of the CO2 and H2O are both 0.25 atm. The equivalent mean hemi- spherical beam length, L, is

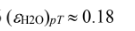
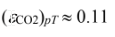
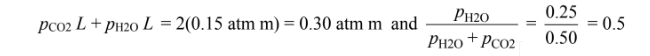
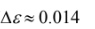
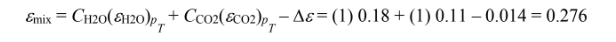
(b) To find the absorptivity to radiation from A1, the emittances of the H2O and CO2 must first be evaluated at T1 = 278 K.
Using the procedure shown above with:
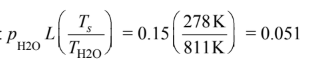
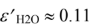
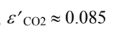
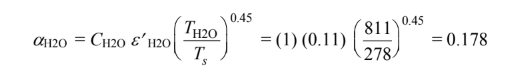
Applying
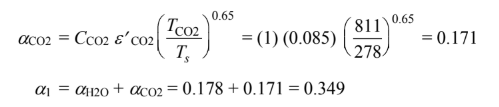
(c) Repeating this procedure for T2 = 1390 K and pH2O L (Ts/TH2O) = 0.257
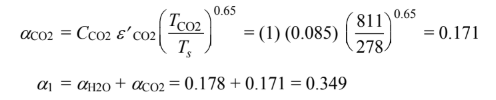
(d) The rate of heat flow from the gas to A1 is
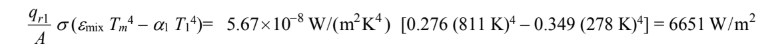
The rate of heat flow from the gas to A2 is
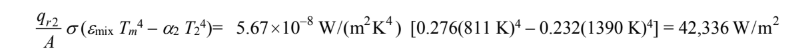
The net rate of heat transfer from the gas is
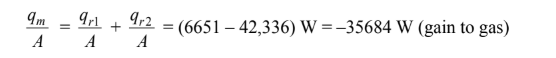
You might also like to view...
A uniform charge density of 500 nC/m3 is distributed throughout a spherical volume (radius = 16 cm). Consider a cubical (4.0 cm along the edge) surface completely inside the sphere. Determine the electric flux through this surface.
A. 7.1 N ? m2/C B. 3.6 N ? m2/C C. 12 N ? m2/C D. 19 N ? m2/C E. 970 N ? m2/C
On an H-R diagram, stellar radii ________
A) decrease from left to right B) are greatest in the lower left and least in the upper right C) increase diagonally from the lower left to the upper right D) are impossible to determine
The resistance to relative motion of two bodies in contact with each other is called __________
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
If an atom has 104 electrons, 157 neutrons, and 104 protons, what is its approximate atomic mass?
A) The approximate atomic mass is 365. B) The approximate atomic mass is 261. C) The approximate atomic mass is 157. D) The approximate atomic mass is cannot be determined with the information given.