The most important factor in decreasing the intracellular concentration of calcium ion after contraction is
A) active transport of calcium across the sarcolemma.
B) active transport of calcium into the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
C) active transport of calcium into the synaptic cleft.
D) diffusion of calcium out of the cell.
E) diffusion of calcium into the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
B
You might also like to view...
The coxal bones articulate with the sacrum at the ________ joint
A) vertebrocoxal B) coxosacral C) iliocoxal D) vertebroilial E) sacroiliac
The fluid link between the external and internal environment is ________.
A) plasma B) intracellular fluid C) interstitial fluid D) cerebrospinal fluid
The triad, seen as structure D, is composed of
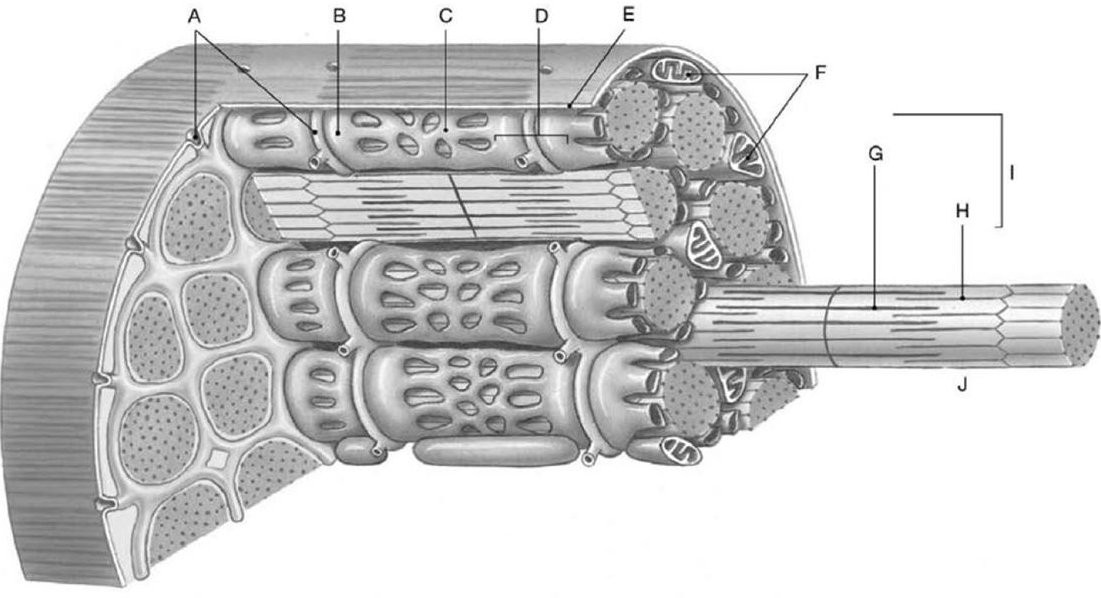
A) the T tubules and the myofibrils.
B) actin and myosin.
C) troponin and tropomyosin.
D) the cisterna of the sarcoplasmic reticulum along with the T tubules.
E) the cisterna of the sarcoplasmic reticulum and the myofilaments.
A neutral atom will become a cation if it
A. loses protons. B. gains protons. C. gains neutrons. D. loses electrons. E. gains electrons.