Assume that an individual consumes two goods, X and Y. The total utility (assumed measurable) of each good is independent of the rate of consumption of other goods. The prices of X and Y are, respectively, $5 and $10. 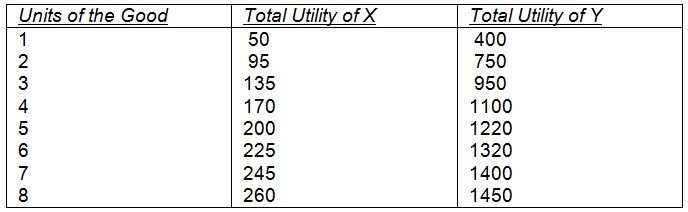 Given the above, if the consumer has $110 to spend on X and Y, which combination will the consumer choose?
Given the above, if the consumer has $110 to spend on X and Y, which combination will the consumer choose?
A. 7X and 7Y
B. 8X and 7Y
C. 6X and 8Y
D. 7X and 6Y
E. 5X and 4Y
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
In the Brander-Spencer model the subsidy raises profits by more than the subsidy because of
A) the "multiplier" effect of government expenditures. B) the military-industrial complex. C) the forward and backward linkage effects of certain industries. D) the deterrent effect of the subsidy on foreign competition. E) the economies of scale once the company enters the market.
Deviations from interest rate parity occur due to
A) transaction costs. B) government controls. C) political risk. D) All of the above.
Education increases the stock of which factor of production?
A) physical capital B) human capital C) land D) entrepreneurship
You decide that it is time to buy a big family car. The opportunity cost you consider is:
a. the cost of the car. b. the increase in comfort for your family while traveling. c. the return this money would have earned if it was invested otherwise. d. the inconvenience you and your family are bearing on account of your old car.