Opportunity cost is best defined as the:
a. sum of all alternatives given up when a choice is made.
b. money spent once a choice is made.
c. highest-valued alternative given up when a choice is made.
d. cost of a good minus the satisfaction obtained from consuming it.
e. cost of capital resources used in the production of additional capital.
c
You might also like to view...
The natural rate of unemployment is defined as the rate of unemployment that
A) exists only during periods of recession or depression in the economy. B) exists due to welfare and unemployment benefits that reduce potential workers' incentives to find work. C) prevails in long-run macroeconomic equilibrium, when all workers and employers have fully adjusted to any changes in the economy. D) prevails in the short-run macroeconomic equilibrium, before workers and employers have had a chance to adjust to an economic shock.
A permanent increase in a country's money supply
A) causes a more than proportional increase in its price level. B) causes a less than proportional increase in its price level. C) causes a proportional increase in its price level. D) leaves its price level constant in long-run equilibrium. E) causes an inversely proportional fall in its price level.
In the diagram below, the following would be a possible explanation for the difference between PPF1 and PPF2. (Assume the starting point is with all butter and no guns.) 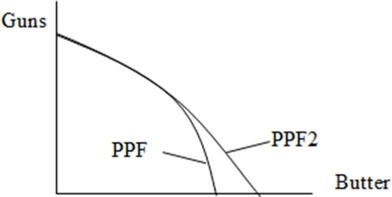
A. A dramatic shock to the resources needed to produce butter. B. A technological improvement in the production of butter and guns. C. A technological improvement in the production of butter. D. A technological improvement in the production of guns.
Which of the following statements about trade is true?
A. Trade often hurts both parties in the long run. B. Trade involves a winner and a loser. C. Trade can benefit both parties. D. Trade is a zero sum proposition.