Explain why the price elasticity of demand varies along a demand curve, even if the demand curve is linear
What will be an ideal response?
As we move down a demand curve, the percentage change in price (quantity) varies. When price is relatively high, a one unit change in price is small in percentage terms. When price is relatively low, a one unit change is much higher as a percent of the price. The same is true for quantity demanded. Given the inverse relationship between price and quantity along a demand curve and the formula for calculating elasticity, as we move down a demand curve, percentage change in price increases and the corresponding percentage change in quantity demanded decreases, causing the ratio of the two to get smaller in absolute terms.
You might also like to view...
Economists define "rational" tastes as those which are objective and transitive. ?
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)
Refer to Figure 5-8. Suppose the emissions reduction target is currently established at 8 million tons. What is the area that represents the cost of eliminating an additional 1 million tons?
A) A + B B) A + B + C C) B + C D) A
Factors that led to worsening conditions in Mexico's 1994-1995 financial markets, but did not lead to worsening financial market conditions in East Asia in 1997-1998 include
A) rise in interest rates abroad. B) bankers' lack of expertise in screening and monitoring borrowers. C) deterioration of banks' balance sheets because of increasing loan losses. D) stock market decline.
Refer to the tables. Assume that before specialization both nations chose to produce alternative B. The gains from specialization and trade would be:
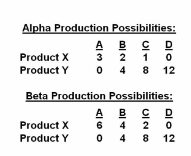
Answer the question on the basis of the following production possibilities tables for countries Alpha and Beta:
A. 2 units of X and 2 units of Y.
B. 4 units of X.
C. 4 units of Y.
D. 6 units of X and 3 units of Y.