All of the following affect the demand elasticity for labor EXCEPT
A) final product income elasticity.
B) ease of substitution of labor for other inputs.
C) final product price elasticity.
D) labor costs as a portion of total cost.
A
You might also like to view...
Which alteration of the assumptions behind the Bertrand model can help avoid the Bertrand Paradox (that an outcome resembling perfect competition may arise with even as few as two firms)?
a. assume firms have limited capacities. b. assume firms produce differentiated rather than homogeneous products. c. assume firms play repeatedly and thus may collude. d. all of the above.
The Phillips curve
a. is the same as a country's production possibilities frontier.. b. is upward sloping. c. illustrates the Fed's choice between inflation and unemployment in the long run. d. illustrates the Fed's choice between inflation and unemployment in the short run. e. illustrates the Fed's choice between inflation and tax revenues in the short run.
In 2009, the top 1 percent of income earners made about
a. 1 percent of all income and paid about 1 percent of all taxes. b. 13 percent of all income and paid about 22 percent of all taxes. c. 22 percent of all income and paid about 13 percent of all taxes. d. 50 percent of all income and paid about 50 percent of all taxes.
Suppose Jordan and Lee are trying to decide what to do on a Friday. Jordan would prefer to see a comedy while Lee would prefer to see a documentary. One documentary and one comedy are showing at the local cinema. The payoffs they receive from seeing the films either together or separately are shown in the payoff matrix below. Both Jordan and Lee know the information contained in the payoff matrix. They purchase their tickets simultaneously, ignorant of the other's choice. 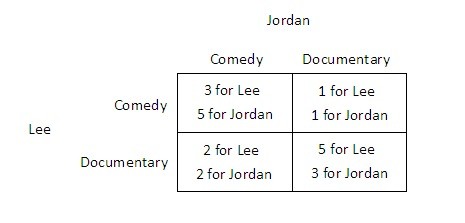 This game:
This game:
A. is not a prisoner's dilemma. B. has no Nash equilibrium. C. is a prisoner's dilemma. D. is an ultimatum bargaining game.