Changes in what frequencies are at the core of how evolution occurs?
What will be an ideal response?
Allele frequencies
You might also like to view...
What nucleotide change is a shared derived character for species A, B, and C, but not for species G?
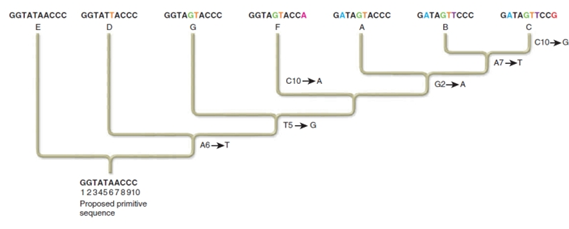
A,T,G, and C refer to nucleotide bases, and the numbers refer to the position of the base in the nucleotide sequences.
For example, A6 refers to an adenine at the sixth position.
A. Changing the second G to an A is common to species A, B, and C, but not to species G.
B. Changing the fifth T to a G is common to species A, B, and C, but not to species G.
C. Changing the second G to a T is common to species A, B, and C, but not to species G.
D. Changing the second G to an A and the fifth T to a G is common to species A, B, and C, but not to species G.
E. None of these show a change in derived characteristics for A, B, and C that are not found in G.
Suppose you want to DECREASE the aggressive behavior of an animal, and all you are allowed to use is a nutritional supplement. Which might be a good choice?
a. increase tryptophan b. decrease thiamine c. decrease lecithin d. increase phenylalanine
Within the phylum Cnidaria, corals are most closely related to:
A. Hydra. B. jellyfish. C. sea anemones. D. Portuguese man-of-war. E. hydrozoans.
What generally triggers the release of calcium ions by ryanodine receptors?
a) potassium efflux b) an action potential c) IP3 uptake d) IP3 release e) sodium influx