Whenever water evaporates,
A) heat is absorbed.
B) heat is released.
C) temperature rises.
D) clouds form.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
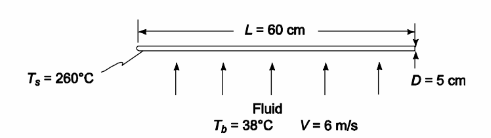
Determine the heat transfer coefficient at the stagnation point and the average value of the heat transfer coefficient for a single 5-cm-OD, 60-cm-long tube in cross-flow. The temperature of the tube surface is 260°C, the velocity of the fluid flowing perpendicular to the tube axis is 6 m/s, and temperature of the fluid is 38°C. The following fluids are to be considered (a) air, (b) hydrogen, and (c) water.
GIVEN
A single tube in cross-flow
Tube outside diameter (D) = 5 cm = 0.05 m
Tube length (L) = 60 cm = 0.6 m
Tube surface temperature (Ts) = 260°C
Fluid velocity (V) = 6 m/s
Fluid temperature (Tb) = 38°C
FIND
1. The heat transfer coefficient at the stagnation point (hco)
2. The average heat transfer coefficient ch for the following fluids
(a) air, (b) hydrogen, and (c) water.
ASSUMPTIONS
Steady state
Turbulence level of the free stream approaching the tube is low
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.0264 W/(m K)
Kinematic viscosity (?) = 17.4 × 10–6 m2/s
Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71
and the Prandtl number at the surface temperature
(Prs) = 0.71. From Appendix 2, Table 32, for hydrogen
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.187 W/(m K) Kinematc viscosity (?) = 116.6 × 10–6 m2/s Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.704 Prandtl number at the surface temperature (Prs) = 0.671
Carbonaceous meteorites contain organic molecules, even amino acids
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Two very small plastic balls of equal mass are released from rest. One of them carries +10 µC of excess charge and the other one carries +1µC of charge
No other charges or fields are present. Which of the following statements are true about them as they move away from each other? (There may be more than one correct choice.) A) The acceleration of the 10-µC ball is 10 times that of the 1-µC ball. B) The balls always have accelerations of equal magnitude. C) The speed of the balls keeps increasing. D) The acceleration of the balls keeps increasing. E) The acceleration of the 1-µC ball is 10 times that of the 10-µC ball.
A piece of copper of mass 100 g is being drilled through with a 1/2" electric drill. The drill operates at 50.0 W and takes 30.0 s to bore through the copper. If all the energy from the drill heats the copper, find the copper's increase in temperature. (ccopper = 387 J/kg • °C.)
a. 40.6°C c. 31.0°C b. 38.8°C d. 27.3°C