The demand for money curve is drawn with
A) the interest rate on the vertical axis and the curve sloping down.
B) the interest rate on the vertical axis and the curve sloping up.
C) nominal Gross Domestic Product (GDP) on the vertical axis and the curve sloping up.
D) nominal Gross Domestic Product (GDP) on the horizontal axis and the curve sloping down.
A
You might also like to view...
Use the following diagram in which S is the market supply curve and S1 is a supply curve comprising all costs of production, including external costs, to answer the question below.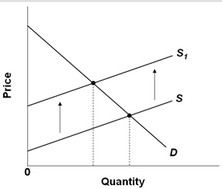 Assume that the number of people affected by these external costs is large. If the government wishes to establish an optimal allocation of resources in this market, it should
Assume that the number of people affected by these external costs is large. If the government wishes to establish an optimal allocation of resources in this market, it should
A. tax producers so that the market supply curve shifts leftward (upward). B. subsidize consumers so that the market demand curve shifts leftward. C. not intervene because the market outcome is optimal. D. subsidize producers so that the market supply curve shifts leftward (upward).
We would expect that a fall in labor supply will have a proportionately smaller effect on the market wage rate when
A) workers can easily be replaced by capital goods. B) the product produced in the industry has very few substitutes. C) the product is produced in a perfectly competitive industry. D) labor represents a relatively small portion of total costs.
In the open-economy macroeconomic model, the key determinant of net capital outflow is the
a. nominal exchange rate. b. nominal interest rate. c. real exchange rate. d. real interest rate.
Using Figure 1 above, if the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD2 to AD3 the result in the short run would be: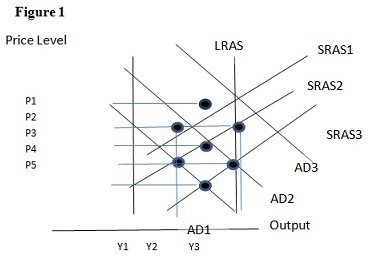
A. P1 and Y2. B. P2 and Y3. C. P3 and Y1. D. P2 and Y2.