Assume that the expectation of declining housing prices cause households to reduce their demand for new houses and the financing that accompanies it. If the nation has low mobility international capital markets and a flexible exchange rate system, what happens to the real risk-free interest rate and net nonreserve-related international borrowing/lending in the context of the Three-Sector-Model?
a. The real risk-free interest rate falls, and net nonreserve-related international borrowing/lending becomes more positive (or less negative).
b. The real risk-free interest rate falls, and net nonreserve-related international borrowing/lending becomes more negative (or less positive).
c. The real risk-free interest rate rises, and net nonreserve-related international borrowing/lending becomes more negative (or less positive).
d. The real risk-free interest rate falls, and net nonreserve-related international borrowing/lending remain the same.
e. There is not enough information to determine what happens to these two macroeconomic variables.
.B
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below.________ inflation will eventually move the economy pictured in the diagram from short-run equilibrium at point ________ to long-run equilibrium at point ________. 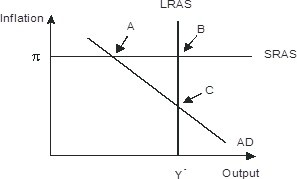
A. Rising; A B. Falling; A; C C. Falling; B: C D. Rising; A; C
Hurricane Katrina destroyed oil and natural gas refining capacity in the Gulf of Mexico in 2005. This drove up the prices of natural gas, gasoline, and heating oil. This is an example of a
A) supply shock. B) demand shock. C) negative externality. D) depression.
The Japanese health care system most closely resembles the health care system of _______, from which it was copied
a. theUnited States. b. France. c. Great Britain. d. Germany. e. Canada.
A constant-cost industry is one in which:
A. the demand curve is horizontal. B. the long-run supply curve is horizontal. C. the short-run supply curve is horizontal. D. All of these