Refer to the table below. Suppose the profit for each unit of paper product is $3.00 and the profit for each unit of lumber is $13.50 and Big Oaks is producing the profit-maximizing quantity of lumber and paper products. If the profit from each unit of paper product increases from $3.00 to $4.00 and the profit for each unit of lumber does not change, to maximize profit, Big Oaks should produce a
________ proportion of paper products and produce ________ units of paper products and lumber.
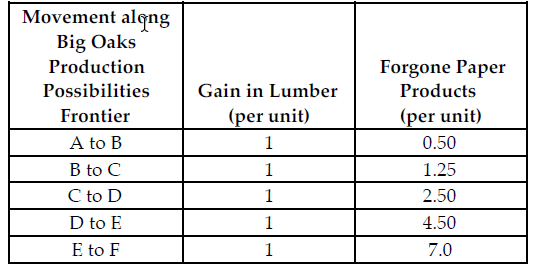
Big Oaks can produce either paper products or lumber with each tree that they harvest. Because Big Oaks can adjust the amount of paper products and lumber they produce from the harvested trees, paper products and lumber are produced in variable proportions. The above table summarizes Big Oaks production possibilities from each harvested tree.
A) smaller; less
B) smaller; more
C) greater; less
D) greater; more
D) greater; more
You might also like to view...
The four-firm concentration ratio
A) indicates the total profitability among the top four firms in an industry. B) is an indicator of the degree of monopolistic competition. C) indicates the presence and intensity of an oligopoly market. D) is used by the government as a basis for anti-trust cases.
A measure of the average price of a given class of goods or services relative to the price of the same goods and services in a base year is called a:
A. real quantity. B. real price. C. rate of inflation. D. price index.
A tax results in ______.
a. unchanged prices and increased production b. reduced prices and increased production c. increased prices and reduced production d. reduced prices and unchanged production
A nondiscriminating pure monopolist finds that it can sell its 50 th unit of output for $50. We can surmise that the marginal:
A. cost of the 50 th unit is also $50. B. revenue of the 50 th unit is also $50. C. revenue of the 50 th unit is less than $50. D. revenue of the 50 th unit is greater than $50.