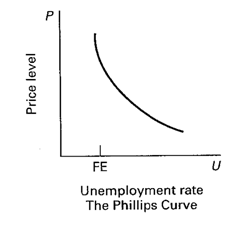
Explain the Phillips Curve concept and construct an example of the curve on the below graph.
What will be an ideal response?
The Phillips Curve concept shows a stable inverse relationship between the rate of unemployment and the rate of inflation. It is based on the idea that as aggregate demand increases in the horizontal range of the aggregate supply curve, unemployment will decline as real GDP rises without an inflationary effect. However, as aggregate demand continues to grow and the unemployment rate approaches full-employment, the price level and real GDP will increase. Finally, at the point of full capacity, only the price level will rise as potential real GDP has been achieved. See graph.
You might also like to view...
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) The demand curve of the perfectly competitive industry is elastic as are the demand curves facing the individual firms. B) The market demand curve of perfect competition is inelastic because the individual consumers are buying a homogeneous product. C) The market demand curve of the perfectly competitive industry is downward sloping while the demand curve of an individual firm is horizontal with a height equal to the product price. D) The market demand curve of the perfectly competitive industry is downward sloping, so the demand curves of the individual firms are also downward sloping.
Merely demonstrating that wages are lower for blacks and females does not in itself prove wage discrimination
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
The temptation of imperfectly-monitored workers to shirk their responsibilities is
a. an example of the moral hazard problem. b. an example of the adverse selection problem. c. an example of screening. d. an example of signaling.
A union can induce a rise in equilibrium wages in a unionized industry by
A. successfully increasing the demand for union labor. B. successfully decreasing the demand for union labor. C. reducing the marginal revenue product of labor to zero. D. reducing the marginal revenue product of firms employing union labor.