When light passes through two or more narrow slits, an alternating dark and bright pattern is observed on a screen because of
a. interference
b. diffraction
c. specular reflection
d. diffuse reflection
e. polarization
A
You might also like to view...
Thermodynamic Processes: In a given reversible process, the temperature of an ideal gas is kept constant as the gas is compressed to a smaller volume. Which one of the following statements about the gas is correct?
A. The gas must absorb heat from its surroundings. B. The gas must release heat to its surroundings. C. The pressure of the gas also stays constant. D. The process is adiabatic. E. It is impossible to predict on the basis of this data.
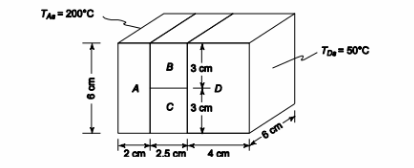
A section of a composite wall with the dimensions shown below has uniform temperatures of 200°C and 50°C over the left and right surfaces, respectively. If the thermal conductivities of the wall materials are: kA = 70 W/(m K), kB = 60 W/(m K), kc = 40 W/(m K) and kD = 20 W/(m K), determine the rate of heat transfer through this section of the wall and the temperatures at the interfaces. including a contact resistance of 0.1 K/W at each of the interfaces.
GIVEN
• Composite wall
• Thermal conductivities:
? kA = 70 W/(m K)
? kB = 60 W/(m K)
? kC = 40 W/(m K)
? kD = 20 W/(m K)
• Surface temperatures
? Left side (TAs) = 200°C
? Right side (TDs) = 50°C
• Contact resistance at each interface (Ri) = 0.1 K/W FIND
(a) Rate of heat transfer through the wall (q) (b) Temperatures at the interfaces
ASSUMPTIONS
• One dimensional conduction
• The system is in steady state
SKETCH
A quantum of light is called
A) a proton. B) a neutron. C) an electron. D) a neutrino. E) none of the above
Equipotentials are lines along which
a. the electric field is constant in magnitude and direction. b. the electric charge is constant in magnitude and direction. c. maximum work against electrical forces is required to move a charge at constant speed. d. a charge may be moved at constant speed without work against electrical forces. e. charges move by themselves.