We assume that in the long run in a perfectly competitive market:
A. the firms can enter or exit.
B. collusion will set in without government regulation.
C. the price will be constant.
D. the number of firms is fixed.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Refer to the below graphs. (Assume that the pre-migration labor force in Country A is 0d and that it is 0u in country B.) If business income is total output minus total labor cost, then business income in country A after the immigration occurs is equal to area:
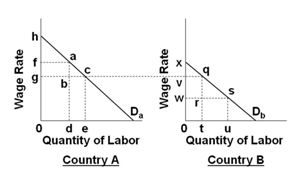
A. haf
B. habg
C. hcg
D. hce0
Answer the following statements true (T) or false (F)
1) To determine the optimal quantity to hold in inventory, a profit-maximizing manager uses marginal analysis. 2) As the quantity held in inventory increases, the probability of selling an additional unit increases 3) The expected marginal benefit falls as the quantity held in inventory increases. 4) As the quantity held in inventory increases, the probability of selling less than that quantity increases. 5) The expected marginal cost decreases as the quantity held in inventory increases.
Which statement is false?
A. Compared to 30 years ago, there is more sentiment in the U.S. for protection against the import of foreign goods. B. The basis for international trade is specialization. C. Our balance of trade has been negative since the early 1900s. D. None of these statements are true.
The price elasticity of demand is calculated by:
A. the change in price divided by the change in quantity demanded. B. the change in quantity demanded divided by the change in price. C. the percentage change in price divided by the percentage change in quantity demanded. D. the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price.